In this article I describe the Data Encapsulation in Networking for CCNA Exam. Data Encapsulation in networking is necessary to know for basic function of packet flow in networking. Data Encapsulation in networking is main part of packet switching in the networking. Ethernet provides connectivity for data flow between the networking devices in a network. An Ethernet provides physical connectivity for data transfer in a network. There are various standards of Ethernet available according to the speed and reliability. The data processing method is known as Data Encapsulation in networking.
Before going to Data Encapsulation in networking, let’s remember the Ethernet basic concepts in networking. Ethernet works on Data link and physical layer of OSI reference model. Data Encapsulation in networking in networking is related to data communication from a device with other devices. The Ethernet provides connectivity between nodes and different networking devices. The most popular Ethernet connector also known as RJ45 connector. Implementation and maintains of Ethernet is very easy. Ethernet port provides speed up to gigabits per second. Ethernet is responsible for formatting, Data Encapsulation in networking and transmission of data in a predefined format. Similarly, at the receiver end the received data reformatted in a predefined format. Data processed at both end transmission and reception end by the Data Encapsulation in networking.
Working of Ethernet at a Glance for Data Encapsulation in networking
Ethernet belongs to IEEE standard IEEE 802.3 family. Data Encapsulation in networking, Ethernet working depends on both physical and data link layer. The Ethernet send and receive the bits and frame in a network. The data frame generated by the process of Data Encapsulation in networking. Physical layer defines the bits streaming and data link layer defines the frame streaming. Ethernet is responsible for VLAN tagging, QOS, error correction and identify the transmission problems. An Ethernet do work metallic conductor cables. Ethernet Cabling Types may be co-axial, twisted pair, CAT-6 cables and optic fibre cable.
Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain depends on Ethernet protocols. Collision and broadcast domain define by the connectivity media like hub, switch etc. The Collision and Broadcast domain defined at different layers of OSI model.
Ethernet basics for networking in detail
Mostly three Ethernet Cabling Types used in a computer network. These three types are important in view of CCNA exam. A lots of networking devices used for creating a LAN. Switches, Hub, Router, Bridge, NIC etc are commonly used in a network. Ethernet Cabling Types are of three types which provides connectivity between networking devices and endpoint devices. The basic Ethernet Cabling Types are Straight-through cable, Crossover cable, Rolled cable and sometimes OFC.
Straight-through and crossover cable generally made of CAT5 or CAT6 cables. Both cables have 4 twisted pair in it. Out of these 4 pairs only two pairs are used for communication in a network. The 4 pairs have distinct colour for identification. CAT5 cable provides data flow speed up to Gigabits per second for a maximum distance of 100 meter. CAT6 cable supposed to provides data flow speed upto 10 Gbps. The purpose of using these different cables is to connect the devices with each other in a network.
Half- and Full-Duplex Ethernet basic concept in networking
IEEE 802.3 standard identify the half duplex Ethernet. In half duplex Ethernet the data flow one side at a time. Suppose two devices are connected with half duplex Ethernet. At one time only one device can send the data. Half duplex Ethernet uses the CSMA/CD protocol. Collision occurs in half duplex Ethernet network. A hub relates to a switch works like a half-duplex Ethernet network. Data flow speed is very low in a half-duplex network due to collision.
Half-duplex Ethernet network uses one pair wire for flow of data in the network. Full-duplex Ethernet works on two pair wire. Full-duplex Ethernet uses point to point connections between sending and receiving device. Full duplex Ethernet network works like a telephone communication. Simultaneously data send and receive in a full-duplex network. Data flow speed is fast in a full-duplex Ethernet network than half-duplex Ethernet network. Each device has its own collision domain in full-duplex Ethernet network. CSMA/CD protocols are used in full-duplex Ethernet network. Full-duplex Ethernet are switch to switch, host to host, router to router, switch to host, switch to router etc.
Data Encapsulation in networking in brief
The process via which data manipulates during flow through the OSI layers is called Data Encapsulation. Some additional bits added to the original data at various layers. These bits are called header and this process is called Data Encapsulation in networking. This process is done on both sides i.e. sender and receiving nodes. In other words, we can say the data changes at every layer of OSI layer.
Each layer uses PDUs for transmit and receive information on OSI layers. PDU is acronym for Protocol Data Units. PDU attached with the header to the data field. Each layer uses different PDU for data encapsulation. Each PDU has its own specific property. The PDU information understood by the peer layer of OSI model. When a layer received encapsulated data from next layer then the layer extracts the PDU and handed over the data to the next layer.
PDU for Data Encapsulation in networking
The below image shows how the PDU attached with data during data encapsulation. You can see at last four layers PDU attached with the data. At transport layer the PDU attached with real data. At transport layer PDU defines the port address. The data breaks into packet from segment and PDU attached with each packet at transport layer. The packets transferred to Network layer. The packet consists of port no. for source and destination at the header. The packets transferred in a sequential way.
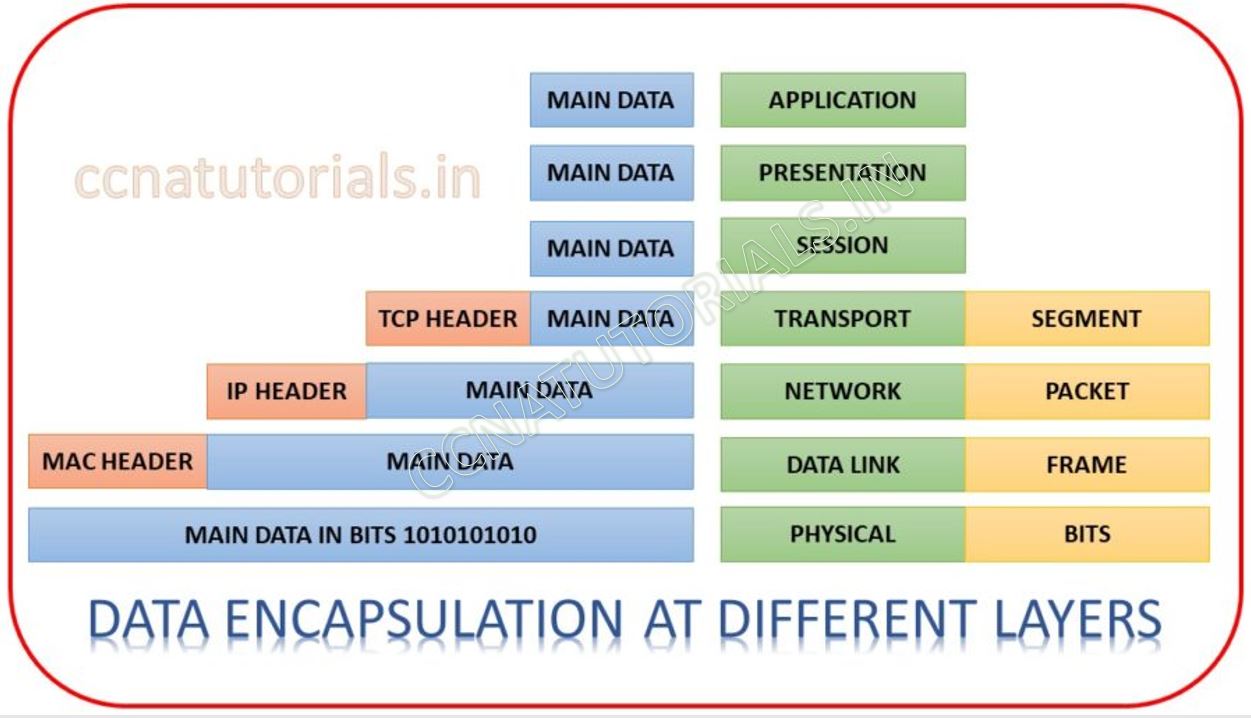
Details of Data Encapsulation in networking at different layers shown in above image
At Network layer the received packets break into small frames. A PDU header attached with each frame. The PDU header consist the IP address of source and destination. The frames transferred to data link layer in a sequence. At data link layer the frame received from network layer.
Data link layer breaks the frames in to bits. A stream of bits is transferred to physical layer. The PDU attached with each frame consisting the MAC address of source and destination. This data with PDU transferred to physical layer.
Physical layer transmits the bits to physical media. At the receiving end reverse process done at each layer.
Explanation of Data Encapsulation in networking
At the transmitting device the data flow from application layer towards physical layer. The first three layer handle the data in its real form. At top 3 layers the data encryption and format changes that is not a part of networking. Data encapsulation starts at transport layer. As shown in below image data received in the form of segment from the session layer.
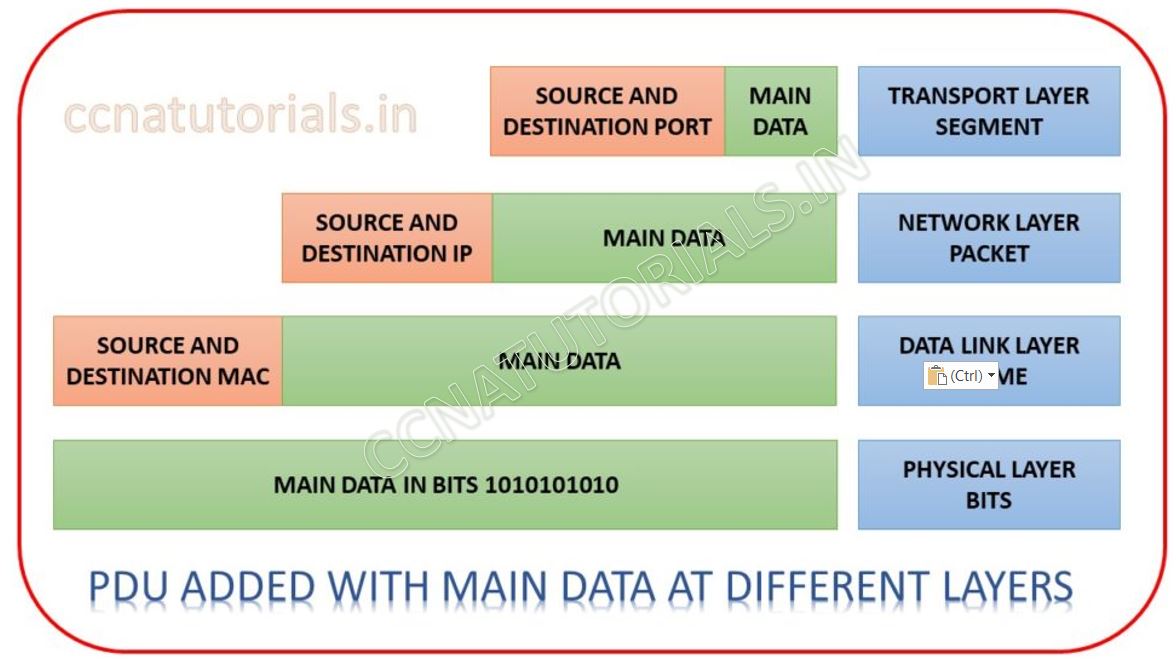
Data Encapsulation at transport layer
At transport layer during transmitting data, the segment breaks in to packets. A header added to each packet. This header consists the port address of source and destination. Ports are used for various services on the same IP address. For example, http works on port 80 and https works on port 443. The PDU attached with packet defines the service for the data. During reception transport layer check the port address at each packet and make segments. Then the segment transformed into the real data.
Data Encapsulation at network layer
At network layer during transmitting data, Packets received from transport layer. Each packet contains a header PDU in which the port address is bind. Network layer breaks each packet into frame and add a PDU header. This PDU header consist the IP address of source and destination. A stream of frames transferred to data link layer. During receiving the data network layer read the IP address in each PDU and forward the packets to the destination IP address. This work is done by a router in a network. That’s why a Numbers of computer work in a LAN send and received their relevant data from a single router gateway. At the time of transmitting data this process is called data encapsulation and during receiving data it is called data de-encapsulation.
Data Encapsulation at Data Link Layer
Data link layer received packets from network layer. These packets contain two headers which are added by above two layers. These headers contain the information of port address and IP address. Data link layer is not related to these PDU in any way. Data link layer attached its own PDU during transmission and de-attached the PDU during reception of data. When transmitting data packets breaks up into frame. A header added to each frame. Data link layer work on MAC address for example layer 2 switch. PDU containing MAC address added to each frame at data link layer. A stream of PDU added frames transferred to physical layer. During receiving data, the stream of bits received from physical layer and frame constructed. MAC address deducted from the header and frames transferred to network layer.
Data Encapsulation at Physical Layer
A stream of frames received from data link layer. Physical layer breaks the frame in to digital signal or bits. Converted bits are transmitted over the physical media. During receive data, the physical layer constructs frame from the received bits and handed over to data link layer.
In this article I describe the Data Encapsulation in networking which includes the Ethernet Basic concepts. I hope you found this article helpful. For any query or suggestion you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.




Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I am very glad to see such magnificent info being shared freely out there.