In this article I describe the Types of IPv4 address in computer networking for CCNA Exam. IP address system in TCP/IP model is the identity of any device in the network. Without IP address any device cannot communicate with the network or other devices. IP is acronym of Internet Protocol. In any network the devices are identify by its unique IP address.
IP protocol works on internet layer in TCP/IP model. Types of IPv4 address in computer networking created by fix length binary numbers. The Types of IPv4 address in computer networking is a logical numeric address allotted to devices in the network. MAC address is the hardware address and never change in any network.
The IP address can be changes for each device in a network. Types of IPv4 address in computer networking was designed to allow hosts to communication with each other. IP system is the identity of any hardware device for communication in the network. The IP address system is of two types IPV4 and IPV6. Here in this article we discuss about IPV4 only. There is a separate article for IPV6 on this website, you can see it here.
Terminology for Types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Before going to explain Types of IPv4 address in computer networking. Some terms are necessary to know which are used in IP address system in computer networking. A Bit may be either 0 or 1. One Byte is equal to 8 bits. One Octat is equal to 8 bits and. Network Address is the designation used in routing protocols for sending the data. It is basically the first address of any subnet.
Network address never used by any device. Network address is the identity of any network. Broadcast Address is used to send data to all nodes in a network. Broadcast address is the last IP of any subnet. In any network address and Broadcast address never assigned to any device. For example 192.168.1.3/24 IP belongs to Network ID 192.168.1.0/24 and Broadcast ID is 192.168.1.255/24.
Network Id is the IP address which use to identify the network. The first IP address of a block of IP address is known as network Id. The last IP address of the IP block is known as broadcast ID. For example 192.168.1.3/24 IP belongs to Network ID 192.168.1.0/24 and Broadcast ID is 192.168.1.255/24.
Structure of IP address system in types of IPv4 address in computer networking
We have approx 232 IP by using 32 bit binary IP which is equal to 4.29 billion approx. These are sufficient to provide connectivity to devices worldwide. We got sufficient IP to use but the problem is that how a Router can store 4.29 billion address in its routing table.
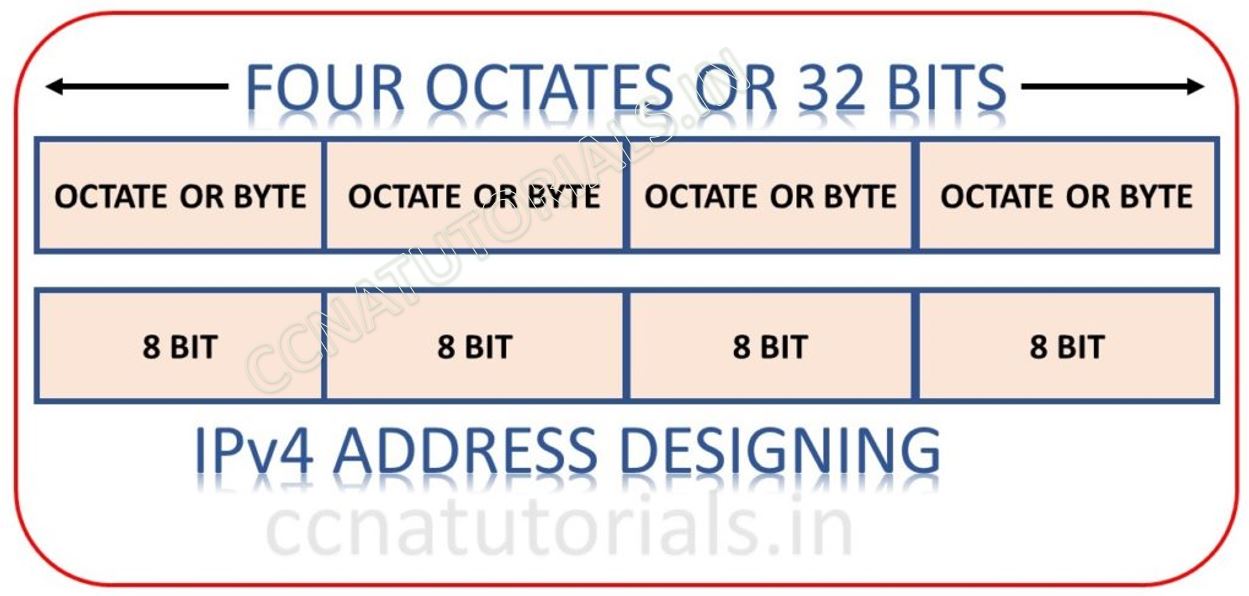
If each router in world keep these all address in it then the data flow speed become very slow. To overcome this problem IP is further divided into network and host part. Subnetting is come to picture to avoid this problem. Class or IP defines by dividing the IP into network and host segments.
Public IP address system in types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Public IP address are those address which are used by internetwork devices for routing protocol. The public IP address are allotted by the ISP of special requirement. When we take an internet connection the ISP allot us only a single public IP which works like a gateway for our small network. Let’s take an example of our home network.
There is a single gateway allotted to us by the ISP in the modem. Behind the modem we are using multiple devices to access the internet. When we add a new device we never ask to ISP to allot a new IP address.
So the scene is that we always working with private IP address in our local network behind a single public IP address. Now let’s move on the topic related to private IP address in computer networking.
Private IP address system in types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Private IP address system in types of IPv4 address in computer networking are a slot of IP address which allow any organisation to create their own private network. These private networks are purely creates for the related organisation for personal use. A single group of IP address can be used by many organisations simultaneously. This is possible because the private IP address series does not configure in any routing table in all over the world. So the routing devices does not identify the devices which are using the private IP address in computer networking.
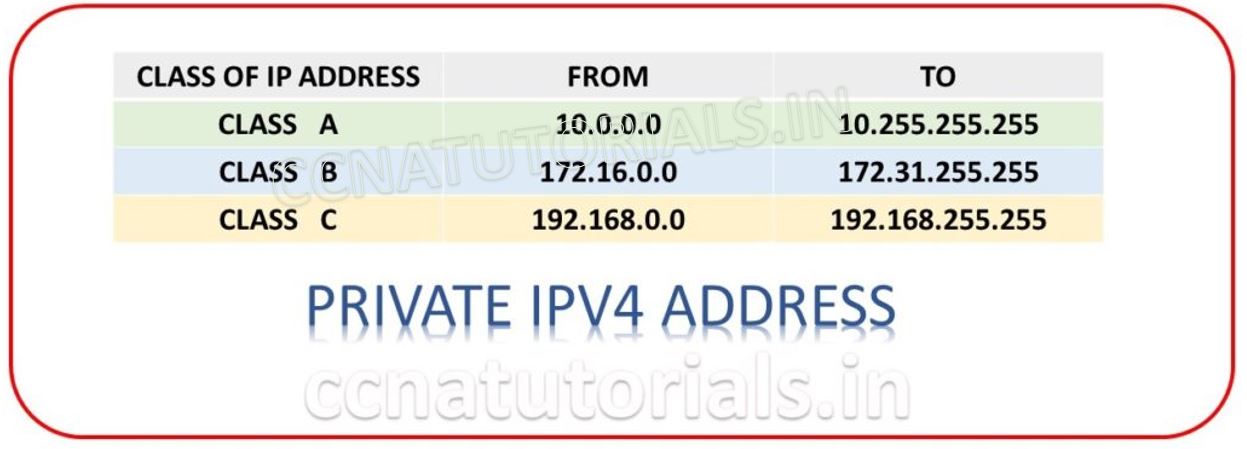
I hope you have seen most of devices at your home or offices are using the common IP series of 192.168.x.x . This IP series is purely allow to use for private devices. Now the question comes in picture how we access internet from these private devices. Well we go on the operation of private IP address later in this article. Now just understand that private devices cannot communicate in an internetwork without routing device such as router.
Reserve IP address system in types of IPv4 address in computer networking
We know the IP addresses are limited and the users are growing day by day. So some IP address keep reserved for some special purpose. These IP address does not used by any networking device.
- All Network address bits are 0 denotes the network itself.
- All Network address bits are 1 shows that all networks.
- IP address 127.0.0.1 reserved for testing purpose locally. Any packet with header 127.0.0.1 never send to in any network.
- All host address bits are 0 denotes to any host.
- The host address bits are 1 denotes to all hosts.
- The network and host bits are 0 denotes the default route in routing protocols.
- The network and host bits are 1 denotes the broadcast for every host.
Loopback address is used to testing the localhost. Pinging IP address 127.0.0.1 well return a reply from local machine. The condition is that software firewall should be off. Firewall always drop the ping packets by default. Most use of 127.0.01 IP address is to check the local hosted website. If you have hosted any website in your local computer then 127.0.0.1 URL display the local hosted website.
Network Addressing for types of IPv4 address in computer networking
In any IP some bits keep fix to define network address. Remain bits are changeable and used for Host. For example in IP 192.168.1.0/24 first three byte remain same for each device in this network. 192.168.1 Remains unchanged 192.168.1.0 is the Network Id and 192.168.1.255 is broadcast address. There can be 252 devices connects in this network. 252 devices can use the IP addresses from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254.
In four bytes we can fix either first Octate for network or first two Octate or first three Octate. IP Class is also defining by the network bits. It is depends on your network how many hosts you want to join in the network. For small number of network and large number of host Class A network created. For large number of networks and small numbers of host class C network created.
Layer 2 broadcast for types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Switch works on layer 2 in a network. Layer 2 flow the data on MAC address basis. There is no need of IP address to broadcast any traffic at layer 2. MAC address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF is use for broadcast at layer 2 in a network. Every device know this MAC address and receive the data. Every device will receive the layer 2 broadcast frame even router. Router will drop these frames because router works on layer 3.
Layer 3 broadcast for types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Broadcast IP address is reserved in every network. Broadcast IP address is the last IP address of any network. For example, the broadcast Ip address for network 192.168.1.0/24 will be 192.168.1.255. This IP will never be used by any host in this network. Broadcasting at layer 3 provides the data for all hosts in a network. DHCP uses broadcasting to dynamically assign IP addresses to hosts in a network. Layer 3 broadcast packet sent to all the devices in the same broadcast domain.
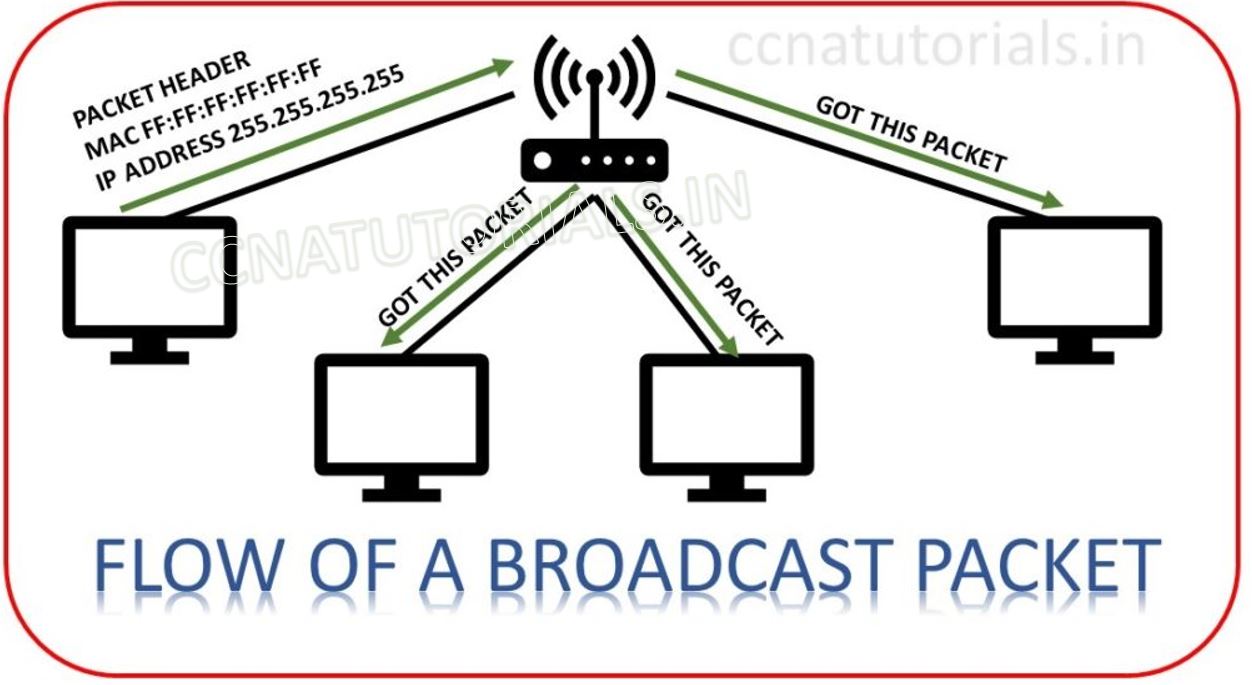
As shown in above figure all hosts on the LAN will get broadcast on their NIC, including the router. The router would never forward this packet.
Unicast IP address for types of IPv4 address in computer networking
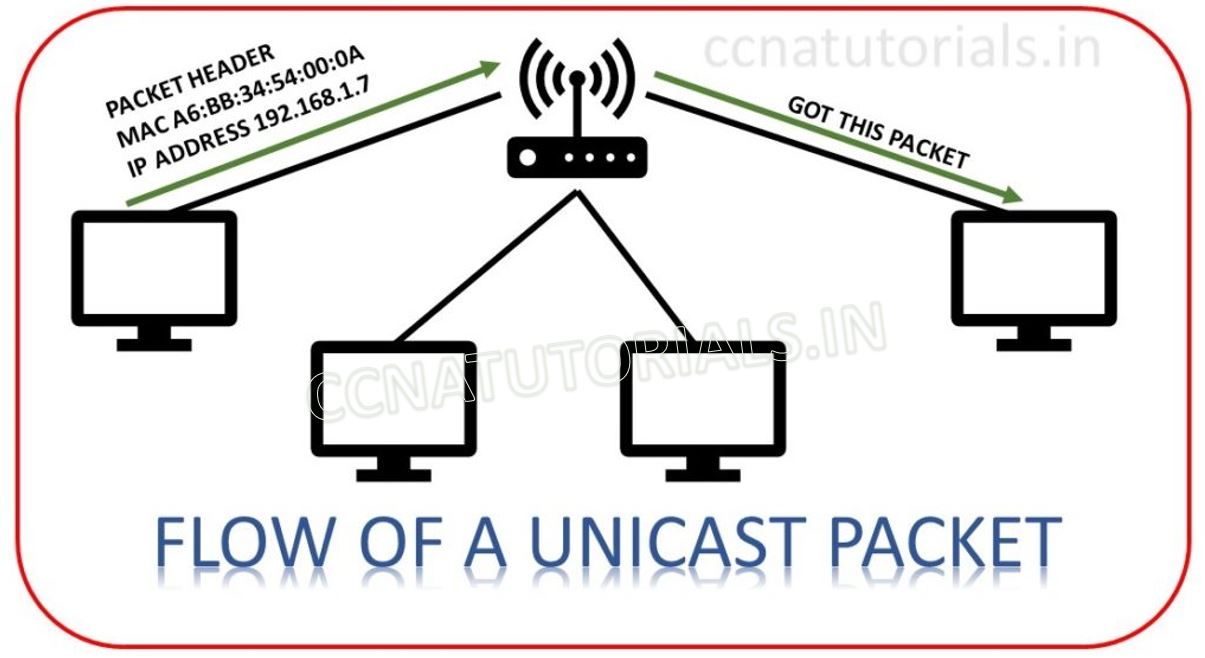
Uni-cast IP address is used for a particular host in a network. An Uni-cast address can be used by a single host for a single host. Uni-cast address identifies a network device like a particular server. This is also known as one to one. See the image below here MAC and IP address belongs to a particular device.Only device 10.1.12 will accept the packet. All other devices receive but not accepts the uni-cast packet.
Multicast IP address for types of IPv4 address in computer networking
Multicast packets sent to many devices at a time on different networks. This is also known as one to many. Multicast also provides point to multi-point communication. Router receive the multicast data and forward a copy of each packet to all interfaces. The range of multicast addresses starts with 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. EIGRP protocol is the best example of multicast IP address.
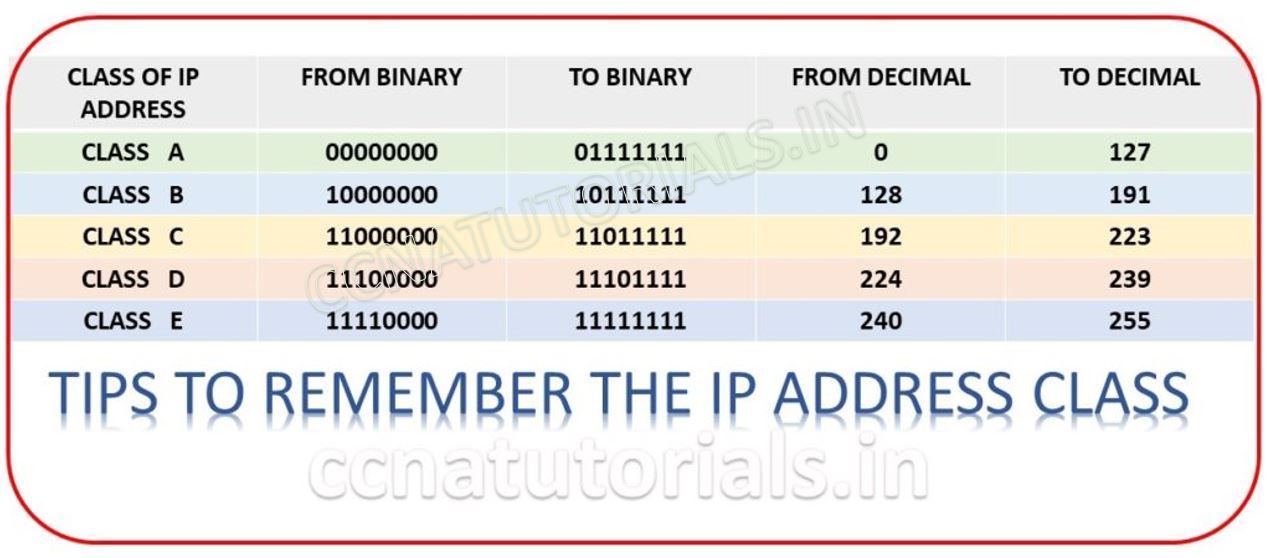
Class A address in types of IPv4 address in computer networking
IP address is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class A network the very first bit remains unchanged and should be 0. All remains 31 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first Octate looks like 0xxxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class A in IP system is from 00000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 011111111.11111111.11111111.1111110
In decimal it denotes 0.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses that’s why 1.0.0.0 and 127.255.255.255 exempted in Class A in IP system. Because they are reserve addresses as discussed earlier.
Class B address in IP address system in TCP/IP model
IP is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class B network the first bit remains 1 and second bit remains 0 of first Octate. All remains 30 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 10xxxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class B in IP system is from 10000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 101111111.11111111.11111111.1111110
In decimal it denotes 128.0.0.1 to 191.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses that’s why 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.255.255 exempted in Class B address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class C address in IP address system in TCP/IP model
IP is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class C network the first 2 bits remains 1 and third bit remains 0 of first Octate. All remains 29 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first Octate looks like 110xxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class C address in IP system is from 11000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11011111.11111111.11111111.1111110
In decimal it denotes 192.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses that’s why 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255 exempted in Class C address in IP s system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class D address in IP address system in TCP/IP model
Class D addresses are reserve for research purpose. In symmetry to above address Classes. In Class D network the first 3 bits remains 1 and fourth bit remains 0 of first Octate. All remains 28 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first Octate looks like 1110xxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class D in IP system is from 11100000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11101111.11111111.11111111.1111110
In decimal it denotes 224.0.0.1 to 239.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses that’s why 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255 exempted in Class D address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class E address in IP address system in TCP/IP model
Class E addresses are reserve for research purpose. In symmetry to above address classes. In Class E network the first 4 bits remains 1 of first Octate. All remains 28 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first Octate looks like 1111xxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class E in IP address system is from 11110000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111110
In decimal it denotes 240.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast addresses consume two IP addresses that’s why 240.0.0.0 and 254.255.255.255 exempted in Class E address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
In this article I describe the Types of IPv4 address in computer networking for CCNA Exam. I hope you found this article helpful related to networking. For any query or suggestion you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.



What i do not understood is in truth how you are now not actually a lot more well-liked than you might be now. You’re very intelligent. You know therefore considerably on the subject of this matter, produced me for my part believe it from numerous numerous angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated except it is something to do with Girl gaga! Your individual stuffs excellent. All the time care for it up!