In this article I describe the Ethernet Frame Format in Networking for CCNA Exam. Ethernet Frame Format in networking is necessary to know for basic function of packet flow in networking. Ethernet Frame Format in networking is main part of packet switching in the networking. The Ethernet provides connectivity for data flow between the networking devices in a network. An Ethernet provides physical connectivity for data transfer in a network. There are various standards of Ethernet available according to the speed and reliability. The data processing method is known as Data Encapsulation in networking. Each data frame have a fix Ethernet Frame Format.
Before going to Ethernet Frame Format in networking, let’s remember the Ethernet basic concepts in networking. Ethernet works on Data link and physical layer of OSI reference model. Ethernet Frame Format in networking is related to data communication from a device with other devices. The Ethernet provides connectivity between nodes and different networking devices. The most popular Ethernet connector also known as RJ45 connector. Implementation and maintains of Ethernet is very easy. Ethernet port provides speed up to gigabits per second. Ethernet is responsible for formatting, Data Encapsulation in networking and transmission of data in a predefined format. Similarly, at the receiver end the received data reformatted in a predefined format. Data processed at both end transmission and reception end by the Data Encapsulation in networking.
Working of Ethernet at a Glance for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
Ethernet belongs to IEEE standard IEEE 802.3 family. Ethernet Frame Format in networking, Ethernet working depends on both physical and data link layer. The Ethernet send and receive the bits and frame in a network. The data frame generated by the process of Data Encapsulation in networking it is necessary to know the Ethernet Frame Format in networking. Physical layer defines the bits streaming and data link layer defines the frame streaming. Ethernet is responsible for VLAN tagging, QOS, error correction and identify the transmission problems. An Ethernet do work metallic conductor cables. Ethernet Cabling Types may be co-axial, twisted pair, CAT-6 cables and optic fibre cable.
Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain depends on Ethernet protocols. Collision and broadcast domain define by the connectivity media like hub, switch etc. The Collision and Broadcast domain defined at different layers of OSI model.
Ethernet basics for networking in detail
Mostly three Ethernet Cabling Types used in a computer network. These three types are important in view of CCNA exam. A lots of networking devices used for creating a LAN. Switches, Hub, Router, Bridge, NIC etc are commonly used in a network. Ethernet Cabling Types are of three types which provides connectivity between networking devices and endpoint devices. The basic Ethernet Cabling Types are Straight-through cable, Crossover cable, Rolled cable and sometimes OFC.
Straight-through and crossover cable generally made of CAT5 or CAT6 cables. Both cables have 4 twisted pair in it. Out of these 4 pairs only two pairs are used for communication in a network. The 4 pairs have distinct colour for identification. CAT5 cable provides data flow speed up to Gigabits per second for a maximum distance of 100 meter. CAT6 cable supposed to provides data flow speed upto 10 Gbps. The purpose of using these different cables is to connect the devices with each other in a network.
Half- and Full-Duplex mode Ethernet basic concept in networking
IEEE 802.3 standard identify the half duplex Ethernet. In half duplex Ethernet the data flow one side at a time. Suppose two devices are connected with half duplex Ethernet. At one time only one device can send the data. Half duplex Ethernet uses the CSMA/CD protocol. Collision occurs in half duplex Ethernet network. A hub relates to a switch works like a half-duplex Ethernet network. Data flow speed is very low in a half-duplex network due to collision.
Half-duplex Ethernet network uses one pair wire for flow of data in the network. Full-duplex Ethernet works on two pair wire. Full-duplex Ethernet uses point to point connections between sending and receiving device. Full duplex Ethernet network works like a telephone communication. Simultaneously data send and receive in a full-duplex network. Data flow speed is fast in a full-duplex Ethernet network than half-duplex Ethernet network. Each device has its own collision domain in full-duplex Ethernet network. CSMA/CD protocols are used in full-duplex Ethernet network. Full-duplex Ethernet are switch to switch, host to host, router to router, switch to host, switch to router etc.
Ethernet Frame Format in networking
Ethernet Frame Format in networking is very important term in Ethernet Basic Concept. Bits combined to bytes and bytes to frames at data link layer. The image below show the Ethernet Frame format. The Frames encapsulates packets at data link layer. Ethernet stations pass the data frames in the form of MAC frame format. This provides error detection from a cyclic redundancy check (CRC). This is error detection only, not an error correction. See the below diagram detail of each section following
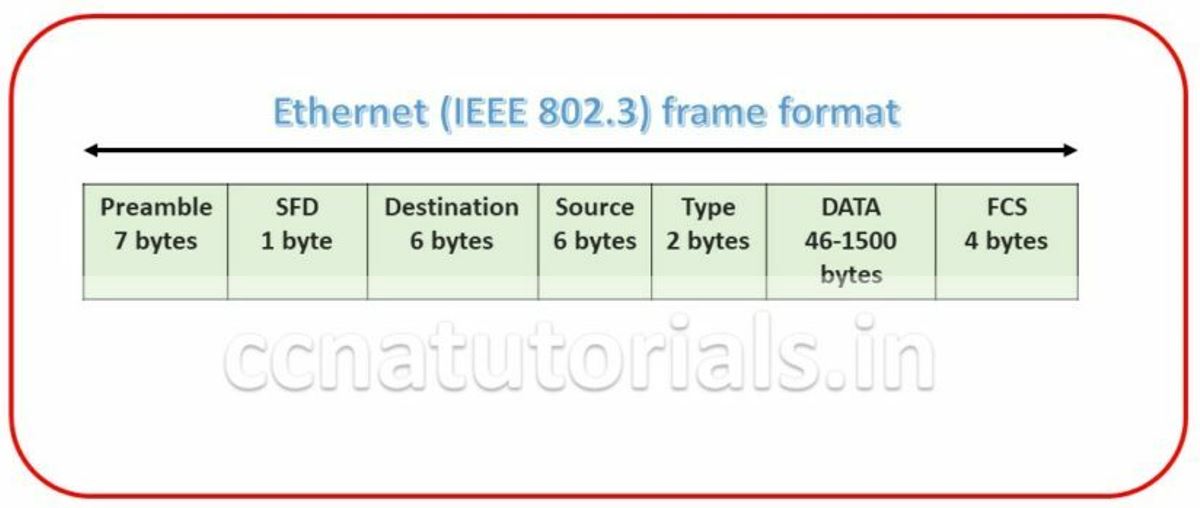
Preamble for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
Preamble is the first section of 7 bytes in a frame. The first seven bytes of the preamble are all the same 10101010. Only one bit even the start one or last one is slightly different like 10101011. The 8 bytes of the preamble and the Start of Frame create a pattern of 64 bits. They are not officially counted as part of the Ethernet frame. The frame begins immediately after the Start of Frame, without a gap. An alternating 1, 0 pattern provides a clock rate at the start of each packet. This allows the receiving devices to lock the incoming bit stream.
Start Frame Delimiter (SFD) for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
The preamble is seven octets and the SFD is one octet. An Ethernet frame starts with preamble followed by the SFD. The actual frame data starts after the SFD. All Ethernet frames starts with the same SFD delimiter, which followed by data unique to the frame.
Destination for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
It is the 48 bits MAC address of the destination. Destination address used by receiving devices to determine the correct destination. By checking the MAC address of device and Destination this work done. This destination addresses also used for broadcasting or multi-casting data in a network. ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff is Ethernet Broadcast address.
Source for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
The source is similar to destination of 48 bits. It is also a MAC address of the source of data transmitting device. These 48 bits source address identifies the sender device. This address can not be all 1s. It is a single addressee MAC address.
Type for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
802.3 uses a Type or length field, but the Ethernet-II frame uses a Type field only. Type field used to identify the Network layer protocol. Network layer protocol may be TCP, UDP or IPX etc.
Data for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
This segment of 46 – 1500 bytes contains the information. This part of the frame will change for each packet. The information required to transmit saved in this section. This packet sent down to the Data Link layer from the Network Layer.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) for Ethernet Frame Format in networking
FCS is the last segment of a frame. It is 4 bytes long only. FCS used to store the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) reply. The CRC algorithm run when each frame built based on the data in the frame. The answers of CRC checked at the receiving station. If the CRC answers not found same the fame discarded and original frame re-transmitted again.
For any query or suggestions on this article contact us or drop a comment below.




There is definately a great deal to know about this topic.
I really like all the points you have made.