Contents of this article
In this article I describe the PortFast and BPDU Guard terms used in networking with Cisco switches. Spanning Tree Protocol STP provide the loop avoidance in a network, where multiple switches are connected with each other as shown in below image. The Spanning Tree Protocol STP is layer 2 protocol of OSI reference model. STP automatically shut down the redundant links which creates the loops. The redundant link creates a loop between switches. STP monitors all links of the network. Spanning Tree Protocol STP finds the redundant link by the Spanning Tree Algorithm. The STA algorithm creates a topology database to find the redundant links.
The Root Bridge is a switch which have lowest bridge priority ID. The Root Bridge switch is the main focus point for all switches in the network. Root Bridge is the main switch of the network. In case the bridge priority value is same in all network switches, the lowest MAC ID use to select the root bridge. In Cisco switches the default bridge ID remains 32768. This Bridge Id can be manually changed. So if you want to make a particular switch root bridge, you need to change its bridge id. Every time when network topology changed the root bridge may be changed. I mean when a new switch added to network or any existing switch removed from the network. In case of failure of Root Bridge, remaining switches automatically select the next root bridge.
PortFast and BPDU Guard
PortFast and BPDU Guard are two different terms related to STP. PortFast is a standard of 802.1D which is a proprietary of Cisco. We know when the switchports changed their stat it will take some time known as convergence. Generally the convergence time is upto 50 seconds. PortFast reduce the convergence time for a very little time which is negligible. So this is cool feature what any network administrator want to maintain a network. PortFast property useful in some special services like DHCP.
PortFast and BPDU Guard explained in details
PORTFAST :- We know the STP enabled switchports take some time during moving from blocking state to forwarding state. There are many network services (like DHCP) required to connect with network devices before they will time out. So we require to stop the STP feature for these networking services on particular switchports. PortFast feature enables a switchport to enter in STP forwarding state immediately. In other words we can say PortFast feature bypass the listening and learning states. PortFast can be applied on any physical or logical port of a switch. PortFast feature configured on the enter or exit ports towards network generally. These enter or exit ports are generally access ports.
PortFast feature do not disables STP service. Remember one more thing the BPDUs can be received on the port after enabling the PortFast feature on a switchport. When a BPDU received on a PortFast port the port changes to a non PortFast switchport.
Configuration of PortFast in a switch
Imagine a scenario where three switches are connected with each other via trunk ports. A DHCP server connected with a switch on port Fa0/1 via access port. Similarly a PC is connected with the same switch on port Fa0/2. See the image below.
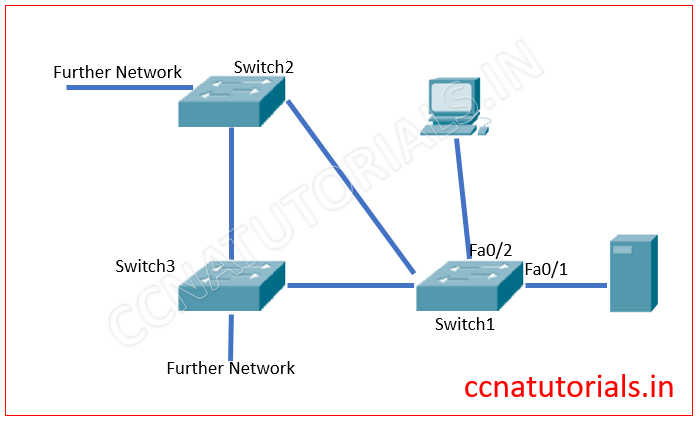
We can see the requirement of switchport Fa0/1. Switchport Fa0/1 required to come in forwading state immediately because it will send the IP addresses to network devices. So in switch1 run the below commands.
switch1>enable switch1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#spanning-tree ? mode Spanning tree operating mode portfast Spanning tree portfast options vlan VLAN Switch Spanning Tree switch1(config)#
You can see in above command window there is a PortFast option available with spanning tree command. This option allows you to use the various features of PortFast mode. Let’s see the option available for PortFast mode.
switch1>enable switch1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#spanning-tree portfast ? bpdufilter Enable portfast bdpu filter on this switch bpduguard Enable portfast bpdu guard on this switch default Enable portfast by default on all access ports switch1(config)#
In above command we can see there are three options available bpdu filter, bpdu guard and default. In case you are using the spanning tree portfast default, all the ports will change to portfast mode automatically. So In this scenario we require to made PortFast to only port Fa0/1. To do these changes run the below commands in CLI mode of switch.
switch1>enable switch1#config t switch1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 switch1(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast %Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops. Use with CAUTION %Portfast has been configured on FastEthernet0/1 but will only have effect when the interface is in a non-trunking mode. switch1(config-if)#exit switch1(config)#exit switch1# %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console switch1#wr Building configuration... [OK] switch1#
By running above commands you can see the message prompt that FastEthernet0/1 has been configured. Similarly you can disable or enable PortFast on any port of the switch.
BPDU Guard
PortFast change the property of any switch port to avoid convergence time. BPDU Guard allow to block receiving the BPDUs on a particular port. When a port receive the BPDU it will converts to non-PortFast mode. So it is necessary to block the receiving of BPDUs. It is not necessary to make BPDU guard port when PortFast is enable, but it is good practice to do that. BPDU guard have two mode to configure one is default and another is globally.
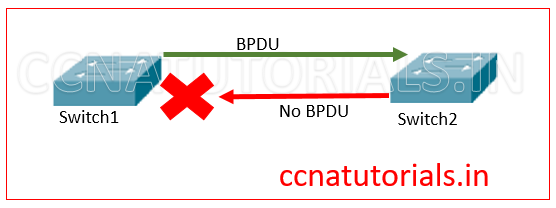
So run the below commands to enable BPDU Guard on all ports globally
switch1>enable switch1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default switch1(config-if)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] switch1(config-if)#
After running above command BPDU Guard set on all switchport globally. To apply BPDU Guard on a particular port run the below command.
switch1>enable switch1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 switch1(config-if)#spanning-tree bpduguard ? disable Disable BPDU guard for this interface enable Enable BPDU guard for this interface switch1(config-if)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable switch1(config-if)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] switch1(config-if)#
That is all about the PortFast and BPDU Guard in networking. Another term BPDU Filter is used in STP configuration. BPDU Filter allow some specific ports for sending or receiving BPDUs.
I hope you understood the purpose and configuration of PortFast and BPDU Guard. For any query or suggestion on this article you may contact us or drop a comment in the below comment form. Share this article if you found this helpful.





