Contents of this article
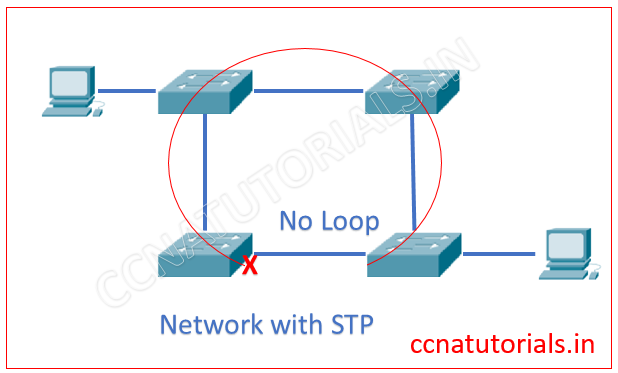
In this article I describe the types of Spanning Tree Protocol. Spanning Tree Protocol STP provide the loop avoidance in a network, where multiple switches are connected with each other as shown in below image. The Spanning Tree Protocol STP is layer 2 protocol of OSI reference model. STP automatically shut down the redundant links which creates the loops. The redundant link creates a loop between switches. STP monitors all links of the network. Spanning Tree Protocol STP finds the redundant link by the Spanning Tree Algorithm. The STA algorithm creates a topology database to find the redundant links.
The Root Bridge is a switch which have lowest bridge priority ID. The Root Bridge switch is the main focus point for all switches in the network. Root Bridge is the main switch of the network. In case the bridge priority value is same in all network switches, the lowest MAC ID use to select the root bridge. In Cisco switches the default bridge ID remains 32768. This Bridge Id can be manually changed. So if you want to make a particular switch root bridge, you need to change its bridge id. Every time when network topology changed the root bridge may be changed. I mean when a new switch added to network or any existing switch removed from the network. In case of failure of Root Bridge, remaining switches automatically select the next root bridge.
Types of STP
We know spanning tree protocol STP provides the loop avoidance in a network. Spanning Tree Protocol created by Cisco. There are various types of spanning tree protocol which are used to make a loop free network. In previous article I describe the spanning tree protocol in brief. Spanning tree protocol disable the redundant links in a network. Root bridge switches are responsible for transmitting the BPDUs and block the redundant ports. See the below image how a port blocked for creation of a loop.
Convergence in network
Before going ahead to types of spanning tree protocol it is necessary to know about convergence in network. When a switch power on first time, all ports of switch try to change the mode to forwarding or block mode. I hope you saw the activity or switch when it is power on. All LED became static in orange color for some time. After few seconds the LED become green and data transfer begins from the ports. Same process done when the network topology changed. I mean a new switch added in network or removing any switch. The transformation of ports to forwarding or blocking modes is known as convergence. During convergence the data flow in network stopped. Now go ahead towards the types of spanning tree protocol.
IEEE 802.1D
IEEE 802.1D also known as common spanning tree (CST). It was developed by IEEE. In this types of spanning tree protocol only one root bridge elected on whole topology. The traffic flow in this topology is slow than the others because the path of traffic is fix towards the root bridge. We can say the traffic flows on the same path. It takes 40 to 50 seconds for convergence process. The main advantage of 802.1D is that it requires Less CPU and memory.
IEEE 802.1S
IEEE 802.1S also known as Multiple Spanning Tree (MST). In this type of spanning tree protocol grouping of all VLANs created for each single group. We can say IEEE 802.1S spanning tree protocol run over another spanning tree protocol. It is highly redundant.
IEEE 802.1W
IEEE 802.1W is also known as Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). The convergence time of RSTP is faster than CST. It allows only one Root Bridge for single network.
Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST)
Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) developed by Cisco for Cisco devices. PVST defines one root bridge per VLAN. It is also a default version of Spanning Tree Protocol. It works on separate 802.1D spanning tree for each VLAN in the network. The bandwidth consumption is less than common spanning tree.
Rapid PVST Rapid PVST is similar version of RSTP or 802.1W. It provide separate instance 802.1W for each VLAN. It provides fast traffic flow in the network. The network convergence time is less than other CST.
I hope you found this article helpful related to spanning tree protocol STP. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.





