In this article I describe the RIP Routing Information Protocol in computer network for CCNA exam. RIP Routing Information Protocol is related to application layer of TCP/IP Suite model. The RIP Routing Information Protocol works for routing on the routers on internet. RIP Routing Information Protocol forward the packets between different routers. RIP Routing Information Protocol provides the connectivity between different networks for data packets flow from one network to another network. The RIP Routing Information Protocol is reliable so if any one link of router goes down. RIP Routing Information Protocol reinstates the communication from another link of the edge router. A standard routing table maintained by the routers for data packet flow between different networks.
Before going to learn about RIP Routing Information Protocol we need to remember the OSI suite and TCP/IP suite model. There are many manufacturer of computer machine in the market. Initially when computers became single user public computer. The computers communicate with only same brand machines. It happens because there was no any fix standard for data transfer between different devices. It is very difficult to make communication with each other when the hardware are of different brands or company. In this article I describe the some basic part of OSI reference layer and TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts in networking with the RIP Routing Information Protocol.
OSI reference model basic concepts
OSI reference model in computer network followed by various vendors to overcome the compatibility problem. After implementation of OSI reference model in computer network, equality maintains by all manufacturer. In 1970 the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The OSI model meant to create inter-operable network with different manufactured devices. In this article I describe some layered approach of TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts in computer network. Before understanding the TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts it is necessary to know about the 7 layers of OSI reference model because the basic work of each layer described in the OSI reference model. You can read the full article related to OSI reference model in computer networking here.
Importance of OSI reference model for RIP Routing Information Protocol
Before going to know about the RIP Routing Information Protocol. It is necessary to know the function of application layer in OSI model and TCP/IP model. Initially not only hardware but software also not supported for work the different computer brand. It became very difficult for all computer users to working without implementation of OSI reference model in computer network. It is necessary then to make some common protocols for all vendors of computer. Before implementation of OSI reference model in computer network, all vendors implements their own protocols on computer hardware and software.
In networking OSI reference model became helpful. OSI reference model describes the flow of data between nodes in any network. Data from one computer application to another computer application transfer by following some common protocols. The OSI reference layer also become beneficial for troubleshooting the network problems. TCP/IP and Cisco three layered hierarchical model of Cisco became more helpful alongside the OSI reference model.
The Layered Approach in computer network for RIP Routing Information Protocol
The Layered approach was the best way to make equality for all computer devices. Layers are not physical but following some protocols. Protocols are for connectivity, connections, data transfer and more. All manufacturer begin to follow the layered approach for OSI reference model in computer network. The OSI reference model change in TCP/IP reference model and later on Cisco three layered hierarchical model. OSI layer architecture have 7 layers. TCP/IP reference model convert these 7 layers into only four layers. After that Cisco three layered hierarchical model converts these 7 layers into three layers. Some layers combined to work in a single layer.
OSI is acronym for open system interconnection. The OSI is a logical reference OSI reference model in computer network. OSI model helps for data flow between different devices and operating systems. All manufacturer used their own architecture before invention of OSI reference model. It was very difficult to establish data communication between different devices. To overcome this problem international organization for standardization (ISO) created the open systems interconnection (OSI) reference model. OSI reference model make data flow possible between different operating system, devices and hardware. Later the OSI model adopted by Cisco as Cisco three layered hierarchical model.
Structure of OSI reference model related to RIP Routing Information Protocol
OSI reference model in computer network consist of 7 layers. These 7 layers further divided into two groups. First 3 layers works for application communication and remaining 4 layers works for data flow. Application, presentation and session layers define the application communication. Transport, network, data link and physical layers define the data flow. Networking protocols works only on last four layers.
TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts for RIP Routing Information Protocol
TCP/IP is acronym for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP suite model). In this section of the article I describe about TCP/IP suite model basic concepts in detail. TCP/IP suite model is a reference model like OSI layers. Instead of 7 layers of OSI reference model. TCP/IP suite model consist only four layer. All seven layers are merged into four layers only. TCP/IP suite model was designed and implemented by Department of Defence (DoD). TCP/IP developed to preserve data integrity. The main purpose to develop the TCP/IP is to provide security in the network. A lots of protocols works on each layer to provide a secure network.
It is necessary to understood the protocols used in TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts. IP addressing play an important role in TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts. By using the IP address and subnet masking broadcast domain breaks. It will improve the performance of the network. Breaking broadcast domain increase the data flow speed. Here IP stands for IPV4 only. We ignore the IPV6 for some time in this article. It will make it easy to understand the TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts.
A snap of TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts
In the decade of 1970’s TCP/IP suite model developed by DoD. In the initial stage TCP/IP suite model divided into two segments TCP and IP. Later its name registered with combined name of TCP and IP like TCP/IP model. ARPA, the Advanced Research Projects Agency of DoD officially authorized to use TCP/IP suite model. TCP/IP model was working well so it adopted by many organisations. In today scenario it is mostly using reference model for networking. Internet is the best example of using TCP/IP.
RIP Routing Information Protocol explained
RIP Routing Information Protocol is a distance vector protocol which works on application layer. The RIP Routing Information Protocol is an application layer IP routing protocol in TCP/IP network or internet. RIP Routing Information Protocol provides the data transfer facility between different LANs. The RIP Routing Information Protocol is a hop count routing protocol. RIP defines the best path between source and destination LAN. The RIP Routing Information Protocol is a dynamic routing protocol. RIP Routing Information Protocol decide the information sharing method of routers between far away LANs.
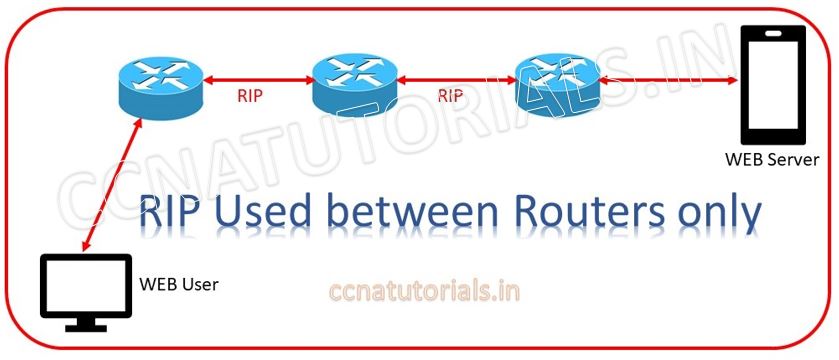
RIP Routing Information Protocol has AD value 120 and uses port number 520. In brief about Routing Information Protocol we discuss in upcoming articles. Here in this article we discuss only an overview of Routing Information Protocol.
Generation of RIP Routing Information Protocol
RIP Protocol was known as GWINFO in the XNS Xerix Network System protocol suite in the decade of 1980. RIP Routing Information Protocol was designed for Xerox PARC universal protocol. Initially RIP used in small network for routing of IP Packets. Due to hope counting limitations this protocol was helpful in small networks. Later OSPF routing protocol used in place of RIP for large networks. RIP Routing Information Protocol have two versions RIPv1 and RIPv2.
RIPv1 Routing Information Protocol version 1
RIPv1 Routing Information Protocol version 1 is a Classful routing protocol. The router updates don’t carry the subnet mask information. RIPv1 doesn’t support the VLSM variable length subnet mask. Because of this limitation it is not possible to maintain subnets of different size in a network. It is required to keep the same size of all subnets in a network. Routing Information Protocol version 1 broadcast updates to 255.255.255.255 every 30 seconds. Every RIPv1 enabled port of router broadcast the updates. These updates carrying the routing table of the router. These updates sent from hop to next hop simultaneously.
Every router listens the updates from its neighbour router and broadcast its own routing table every 25 to 30 seconds. To keep update own routing table the time synchronisation is necessary. RIPv1 support maximum hop count to 15 hops. Any router farther than 15 hops away considered as unreachable for RIPv1 routing protocol.

RIPv2 Routing Information Protocol version 2
RIP version 2 was developed in 1993 to overcome some drawbacks of RIPv1. RIP version 2 declared internet standard 56 in 1998. Routing Information Protocol version 2 carry the subnet information so it is supposed as CIDR Classless Inter Domain Routing protocol. Maximum hop count is like RIP v1 i.e. 15 hops. Keep hop same is to keep it compatible with previous version of RIP Routing Internet Protocol. RIPv2 multicast the update information on 224.0.0.9 to next router. Authentication of RIPv2 updates is also available with RIP version 2 protocol. A new feature of route tags is added in RIP version 2. This feature keep RIPv2 compatible with other routing protocols.

Features of Routing Information Protocol
Update timer is a time function of Routing Information Protocol. Update Timer provides the Frequency of routing updates which is Every 30 seconds. Invalid Timer denotes absence of refresh update from the neighbour router. 180 seconds is holding time without any update. Hold Down Timers is 180 seconds to keep the routing table updated. Flush Timer used to remove the routing table after 240 seconds if there is no any update received from its neighbor. Every 16th hop is treated as infinite hop.
Working of Routing Information Protocol
Each RIP enabled router maintains a routing table. The routing table consist details of destinations routers for a packet passed through it. Routing Information Protocol uses a distance vector algorithm to decide the best path for a packet passed through it.
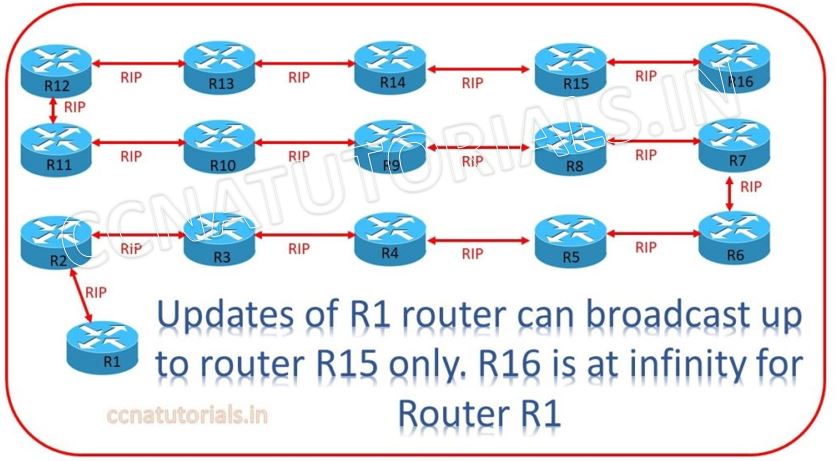
Each router broadcast its entire routing table to the neighbors which are connected directly. Same information along with routing table of second router is broadcast to next hop. The process goes on till the last hop received the update information. After completion of update routing tables all routers have same routing table this is known as convergence.
In this article I describe the RIP Routing Information Protocol in computer network for CCNA Exam. I hope you found this article helpful for any query or suggestions you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.






