In this article I describe the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in computer network for CCNA exam. Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in computer network related to IP address system in networking. VLSM Variable Length Subnet Mask denotes the class of IP address used by the device in computer network. It is not possible to categorise the IP address without using the Subnet Mask in computer network . So we can say Subnet Mask is a part of IP address system in networking.
Before understand the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in computer network you may read about the VLSM Variable Length Subnet Mask. Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR provides the IP routing for a VLSM network. Communication between different devices on a network depends on the type of IP address. The Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR define the IP address Routing for a device. let’s remember the IP address structure in short before understand the Subnet Mask in computer network.
Designing of IP address system
An IP address is combination of 32 bits. Each bit either 0 or 1 but not blank. 32 bits further divided into four Octate. IP can be written in two formats Binary or Decimal. Computer change the decimal into binary during communication. Example of IP in decimal is 10.0.0.0 same in binary 00001010.00000000.00000000.00000000 . User not used the IP in binary system. It is not easy to remember a 32 bit long binary number. During configuration in devices or routing we use the decimal format of IP . Some times IP is also written in Hexadecimal. We discuss about decimal and binary format in this article.
Subnet Mask in computer network
The IP address consist network address and host address. Subnet Mask in computer network denotes the network and host part in a IP address. Subnet Mask in computer network can be used to identify the class of IP address. We can separate the network and host ID on the basis of given Subnet Mask. In case of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR we can define the VLSM Variable Length Subnet Mask according to our requirement. Suppose you have only 25 system in your network then you can use the VLSM Variable Length Subnet Mask which allow 25 computers to communicate in the network. This practice provide the saving of time and reliability in the network.
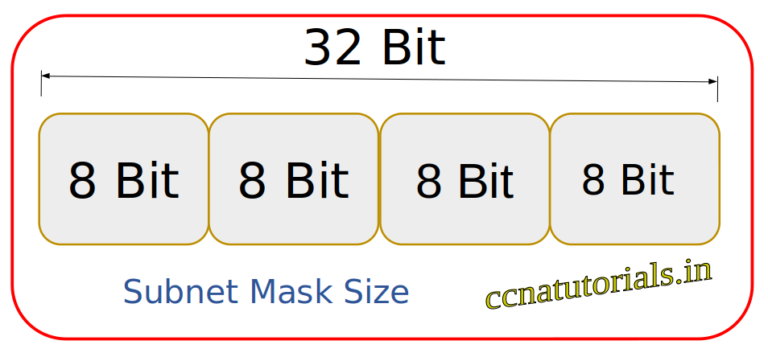
The Subnet Mask in computer network is a 32 bit and 4 octate number combination similar to IPv4 address system. The bits which are 1 denotes the network segment and the bits remains 0 denotes the hosts segment. So the whole 32 bit IP address can be divided into network and hosts segment by using the Subnet Mask in computer network.
The large network can be breaks into smaller networks by using the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in computer network. We know the data flow in big network is difficult then in small networks. The point of security is also strong in small network comparison to a large network. We can say the small network are more efficient than the large networks.
Subnet make it easy to identify the class of network. Class A, B and C uses default subnet masks “255.0.0.0”, “255.255.0.0” and “255.255.255.0” respectively. The above values are fix for classfull system. When we working in VLSM( Variable Length Subnet mask) and CIDR (Classless Inter Domain Routing) the subnet has not fix value. We can say there is no class in the network.
Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR
Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR generally known as supernetting which provides the IP address to work beyond the basic classes of IP address. The basic classes of IP addresses are Class A, B,C network. The main purpose of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR is to reduce the wastage of IP addresses. We can save the IP address by using only required IP addresses for communication.
This can be done by using the VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR only. Classful IP address system consume a complete range of IP addresses. We need only some limited IP address for a network. To avoid the wastage of IP addresses VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR works efficiently. A Class C network allow to use maximum 254 hosts in the network. In case we need only 20 IP address there is no way in the classfull scheme to extract 20 IP address. To avoid these boundations VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR provides the classless IP address scheme.
Classless Inter Domain Routing is commonly used in present days. Classless Inter Domain Routing required when users of internet increased and IP address are limited. Firstly the IP address are classified in 4 major classes. These are A, B, C and D class. Allotment of IP address according to classes is not possible. Requirement of IP address is depends on the host count in a network.
Purpose of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in computer network
The main purpose of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR is to create small networks in a large network. The devices belongs to a particular VLSM Variable Length Subnet Mask can communicate with other devices in the same subnet mask. We can create small networks which can work without interfere each other. Just like VLAN in a layer 3 switch.
Router provide the communication between different subnet mask by using the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR protocol. The size of different subnet may be different in a large network. The subnet creates according to requirement of networks and hosts. It is possible that a subnet have 20 hosts and other subnet have 200 hosts is a same network. So before creating subnetting we need the size of subnet and number of hosts.
According to IP address classes number of user are fix for each class. For example in class C network maximum valid host count are 252. What if i need IP address for 500 hosts. Should I take a class B IP schema? No because class B have 65536 hosts and i need only 500. A lots of IP address become waste. To over come this problem Classless Inter Domain Routing invented. There is no fix class of IP address in CIDR or VLSM.
For example the IP address 192.168.10.3 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0 denotes the network id is 192.168.10.0 and the host id is 0.0.0.3. so in this network we can use 256 IP addresses 0 to 255 for hosts. But as we know we have to leave two addresses for network ID and Broadcast ID so we can use 254 device in this subnet of network. The network ID will be 192.168.10.0 and broadcast ID will be 192.168.10.255.
Express the CIDR Classless Inter Domain Routing
We identify the class of network by its subnet mask. Subnet mask 255.0.0.0 is class A network. Similarly 255.255.0.0 is class B network. Actually the subnet mask is a combination of 32 bits and we divided these 32 bits into 4 octate. Each octate defines a class of network. In Classless Inter Domain Routing the 4 octate become only one 32 bit combination.
First on bit represents network and remaining off bits used for host ID. Suppose i need on 10 host ID . Only four bits are sufficient for 10 hosts. CIDR provides the facility to get only last four bits for host. It will be written as a /28 subnet masked network. Similarly for 500 hosts i can use a /23 subnet mask network.
Configuration of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR explained in brief
let’s assume a network which required 300 IP address for its devices. We need class B IP address block, but using Class B for 300 IP addresses waste the remaining thousands IP address. So we need to go classless addrss system. So Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR concept used to decrease the wastage of IP addresses. In Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR we can transfer the bits of host to the nework side. In that case the subnet mask will be changed according to the requirement of hosts in a network. The Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR written as IP/n where IP is IP address and n is number of bits used for network id.
Suppose a LAN required only 5 host and another required 62 hosts. We do simple subnetting for both LAN, /26 provides 62 host ID. In first LAN where only 5 host ID are required /26 make 57 IP address waste. To save these 57 address we use Variable Length Subnet Mask and give /29 mask for first LAN. VLSM can be used in a WAN via router. Below table is example to find the mask according to number of hosts in each subnet.
| Subnet mask | Mask in decimal | Valid Host counts | Block size of subnet |
| /25 | 128 | 126 | 128 |
| /26 | 192 | 62 | 64 |
| /27 | 224 | 30 | 32 |
| /28 | 240 | 14 | 16 |
| /29 | 248 | 6 | 8 |
| /30 | 252 | 2 | 4 |
Methods to use the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in a network
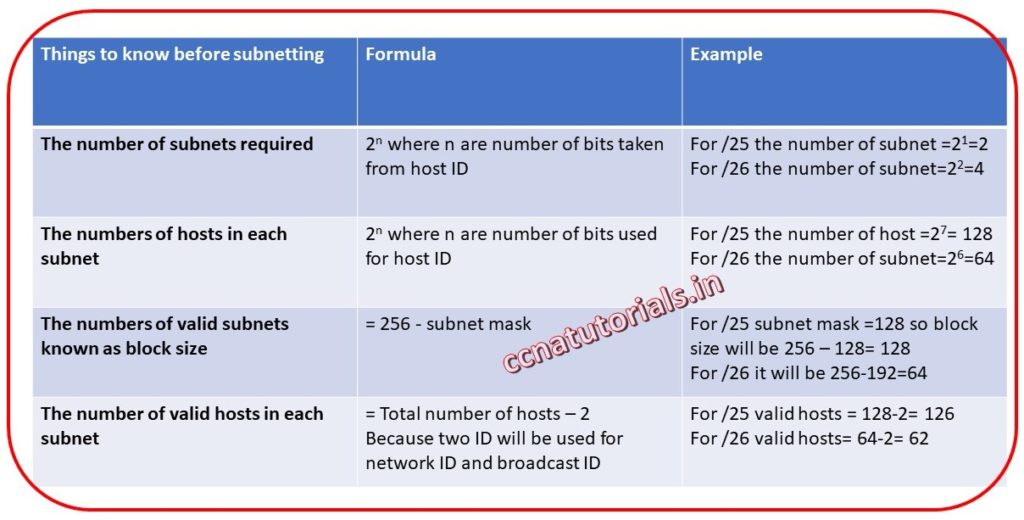
You have to know five things before going to make CIDR in a network.
1. The number of subnets required. How many networks you want to create. In a subnet mask the masked bits are use to know the subnets. For example in a class C address for /26 mask we have 2 bits on and remaining 6 bits are available for hosts. Here number of subnets is 22=4. It means if we use first two bits of host we can create 4 subnets. Similarly for a /27 mask we have 3 bits masked. For /27 we have 23=8 subnets.
2. The numbers of hosts in each subnet. In above para you know the valid subnets by using the masked bits. Similarly to know the numbers of hosts in each subnet can be calculated by using hosts bits. For example for a /26 mask we have only 6 bits for hosts. So here the numbers of hosts ID is 26=64. we have to leave 2 ID for network ID and broadcast ID. So in a /26 mask 26-2=62 hosts per subnet are available.
3. The numbers of valid subnets known as block size. A simple formula is used to get the valid subnets. 256-subnet mask= valid subnets. For a mask /28 the decimal value is “255.255.255.240”. Here the block size will be 256-240=16. So the block size of a /28 mask is 16. It means there are 16 subnets in a /28 mask.
4. The number of valid hosts in each subnet. The simple formula to know the valid host in a subnet is Block size-2= valid hosts. In a 4 block size the valid hosts are only 2 in each subnet. Remaining 2 ID will be used for subnet ID and Broadcast ID.
5. The broadcast address or each subnet. The last address in each subnet will be broadcast address. For example for a /30 mask we have only 22=4 valid host ID. The last Host ID will be used for broadcast ID in this subnet. For example for a block size of 4 the valid host are 1,2 because 0 is the subnet ID and 3 is the broadcast ID. Another example for a 64 block we have 0 to 63 Host ID in first block. So here the broadcast ID for first block will be 63. in next block the broadcast ID is 127 and so on.
Benefits of Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR in networking
Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR save the IP address from wastage. The network size can be reduced by using CIDR. Small network provide a efficient data flow between the devices. Actually Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR is mostly used by the ISP to provide the millions of connection for public use. CIDR support all routing protocols like RIPv2 and OSPF. Some old protocols like RIPv1 do not support the CIDR. All internet gateway used the Classless Inter Domain Routing CIDR to avoid waste IP address.
In this article I describe the CIDR Classless Inter Domain Routing in computer network. I hope you found this article helpful. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below. your suggestions are always welcome by us.