Contents of this article
In this article I explain the configuration of OSPF in single Area. Here single Area means all routers belongs to common area. Before going to configuration of OSPF in single Area let’s revise some common features of OSPF. OSPF is a link state routing protocol. OSPF works at layer 3 of OSI which is known as network layer. Routing devices works on network layer like router.
OSPF uses port number 89 for routing. The Administrative Distance AD is by default 110. OSPF use 224.0.0.5 IP address for multicast and 224.0.0.6 for updates. There are some predefined terms which make OSPF working. OSPF supports both IPv4 and IPv6. These terms are known as OSPF fundamental terminology. It is necessary to understand these terms for CCNA exam.
Wildcard mask for configuration of OSPF in single area
In a LAN the subnet mask defines the network for communication. Suppose I have a network with network ID 192.168.1.0/24. All devices lies in the network 192.168.1.0/24 can communicate with each other. But what if I want to deny only single network and allow all other networks. For example I want to allow all network ID packets in my network except 192.168.1.0/24. In this case I use the wildcard mask to deny all traffic from the network 192.168.1.0/24.
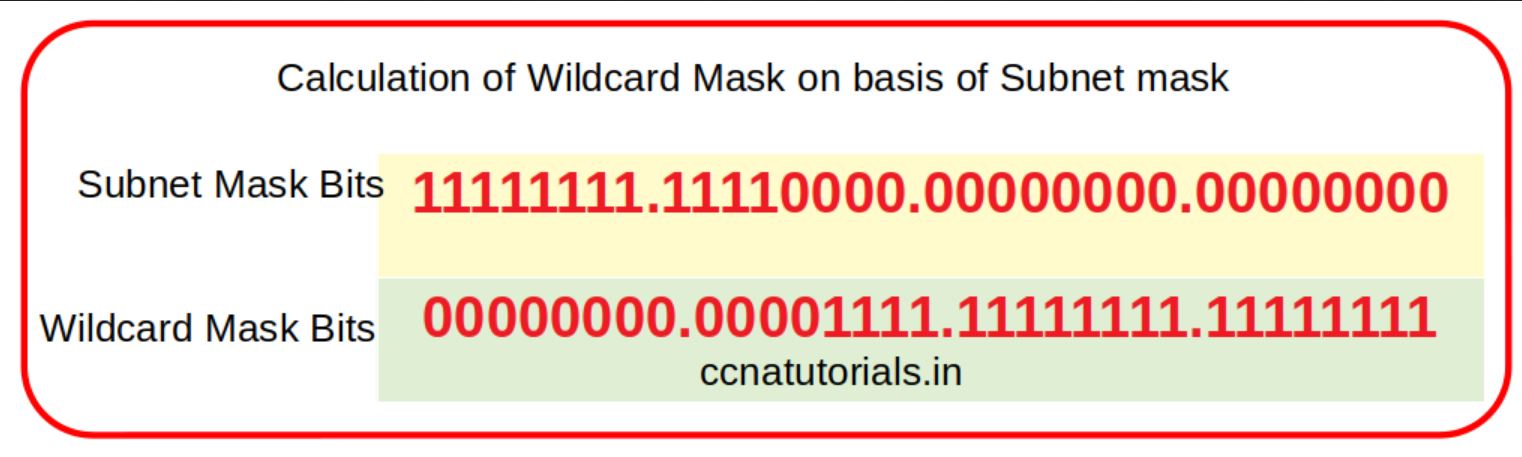
So wildcard mask is inverted value of subnet mask. Just replace the 1 by 0 and 0 by 1 in subnet mask the result will be wildcard mask. For example for network ID 192.168.1.0/24 the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 and wildcard mask is 0.0.0.255. Similarly, for subnet mask 255.255.255.252 the wildcard mask will be 0.0.0.3. Wildcard mask used in configuration of OSPF in single area.
Topology of network required the configuration of OSPF in single area.
To explain the configuration of OSPF in single area I select the network topology as shown in below diagram. There I take three routers connected with each other. A PC is connected with each router. The IP address schema is shown in figure.
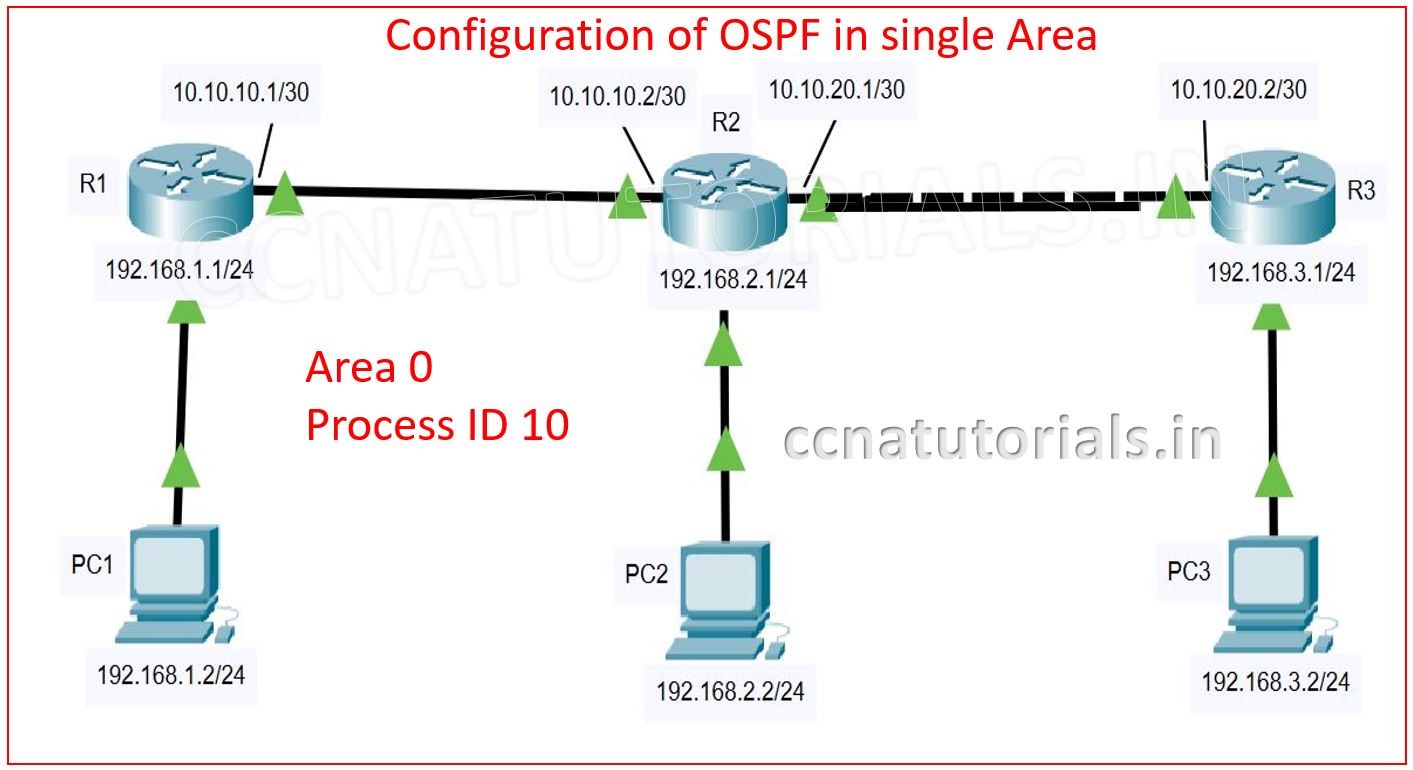
After completion of connectivity we need to assign the IP address to each PC. The IP address and gateway of each PC is set according to the image. After assigning the IP address in PCs we need to configure the routers.
Firstly assign the IP address to different interfaces of the router. To do so run the below commands in CLI of router R1.
Router>en Router#config t Router(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shut R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#no shut R1(config-if)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#
Similarly run the below commands in router R2 to assign the IP address on interfaces of Router R2.
Router>en Router#config t Router(config)#hostname R2 R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)#no shut R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 R2(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#no shut R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0 R2(config-if)#ip address 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#no shut R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK]
Now run the following commands in Router R3 to assign the IP address to each interface.
Router>en Router#config t Router(config)#hostname R3 R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)#no shut R3(config-if)#exit R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 R3(config-if)#ip address 10.10.20.2 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)#no shut R3(config-if)#exit R3(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] R3(config)#
By running above all commands the link of each router is up. The PC can communicate with the gateway. Try to ping the PC with each other you can see the PC are not able to ping with each other. See the commands below in PC1.
C:\>ping 192.168.2.2 Pinging 192.168.2.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Ping statistics for 192.168.2.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss), C:\>ping 192.168.3.2 Pinging 192.168.3.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable. Ping statistics for 192.168.3.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss), C:\>
Now we require to configure the OSPF in each router to make possible the communication in the network. The syntax of OSPF commands is shown in below image.

Here I take the process ID 10 Area ID is 0. So firstly configure the OSPF in router R1. Run the below commands in router R1.
R1>en R1#config t R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)#network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R1(config-router)#exit R1(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] R1(config)#
Now run the below commands in Router R2.
R2>en R2#config t R2(config)#router ospf 10 R2(config-router)#network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R2(config-router)#exit R2(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] R2(config)#
Now run the below commands in Router R3 to configure the OSPF.
R3>en R3#config t R3(config)#router ospf 10 R3(config-router)#network 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R3(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R3(config-router)#exit R3(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] R3(config)#
Checking the configuration of OSPF in single area router.
After configuration of OSPF in routers you can check the routing protocol by running the command “show ip route” command see the example below. Here the bold text show the OSPF routing protocol and the network configured with OSPF.
R1#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.10.10.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 O 10.10.20.0 [110/2] via 10.10.10.2, 00:08:25, FastEthernet0/1 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 O 192.168.2.0/24 [110/2] via 10.10.10.2, 00:08:25, FastEthernet0/1 O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/3] via 10.10.10.2, 00:08:25, FastEthernet0/1
So you can check the OSPF configuration in all routers. Now you can also enable to ping all PCs with each other. See the example of Ping in below command.
C:\>ping 192.168.2.2 Pinging 192.168.2.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126 Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Ping statistics for 192.168.2.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms C:\>ping 192.168.3.2 Pinging 192.168.3.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125 Ping statistics for 192.168.3.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms C:\>
So this is all about the configuration of OSPF in single area. I hope you found this article helpful with practical hand. For any query or suggestion drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.




