Contents of this article
In this article I describe the Access point in networking. Access point is any device which can be accessed by the end user. Generally access point in networking means the Wireless router. The wireless router provides Wi-Fi connectivity to devices to access the network generally internet. Access point have built in router which works as a gateway to internal devices. The wireless access point is a network device which receive and transmit the data on a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network).
Access point is a device which works at Data link layer in networking. An Access point in networking, receive and transmit the data packets between different end devices. Access point inspect the header section of the received packet to check the destination IP address and MAC address then forward accordingly. Access point can connect the computers via Wi-Fi channel, Fast Ethernet port and optic fibre port. Switch works on its operating software which store the MAC address of devices connected with the various interfaces of Access point.
The Access points are always placed behind the gateway device. Router is generally used as gateway device for all data packets of a network. Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch works like a bridge between the multiple devices in a computer network. Switch are used to the basic data packet forwarding function to high end configuration switching. The latest access point are capable to create and works with VLAN in the network. The broadcast domain can break by creating the VLAN in switches.
Access point can be placed anywhere such as home, office and public places. Access point provides connectivity via WiFi to the computers, smartphones and printers etc. Mostly big organisations uses wireless access point to provide the network connectivity to their clients. The clients can work on their computers or laptops with a central network. In today scenario mostly public place offer WiFi access points to public for free. The access point relay the data frames to all 802.11 and 802.3 standard stations on the same subnet.
Access point in networking explained
An access point is a hub which allow multiple devices to connect with each other. The network may be intranet or internet. An access point can be used as extender to increase the network connectivity beyond the wired connection. According to the functionality the access points can be divided into three types standalone, multifunction and controlled access point. Standalone access point allow the devices to connect with it like a standard networking switch. The multifunction access point can provide multiple services like routing, switching and wireless connectivity. The controlled access point is a client device of wireless LAN controller. Let’s discuss about these three types of access points in detail.
Standalone access point in networking
Standalone access point provides simple connectivity to devices for data transfer between them. Standalone access point mostly used within LAN only. When there is no access to internet or any other network, standalone access point mostly used. Basically standalone access point is like a layer 2 switch which receive and transmit the frame packets. It works on MAC address of connected devices. The concept is very similar to the layer 2 switch, it learn and update the MAC address table in it. On the basis of these MAC and IP table the data packets forwarded to the destination devices.

The standalone access point works on the IEEE 802.11 standard. It works on radio signal of 2.4 Ghz or 5 Ghz frequency. The mode of operation is fully duplex. It means it can receive and transmit the data packets simultaneously. The network administrator can bind the MAC address with the device for security reason. It means only those devices can connect with it whose MAC address is saved in its memory.
Multifunction Access Points in networking
Multifunction Access points provide multiple facilities from a single wireless device. The multiple functions may be routing, switching and two different networks connectivity. The multifunction access point can provide the internet access to all devices or some limited devices. It can provide the connectivity of a common printer to all devices in the network. Two different network can be accessed from these type of devices.
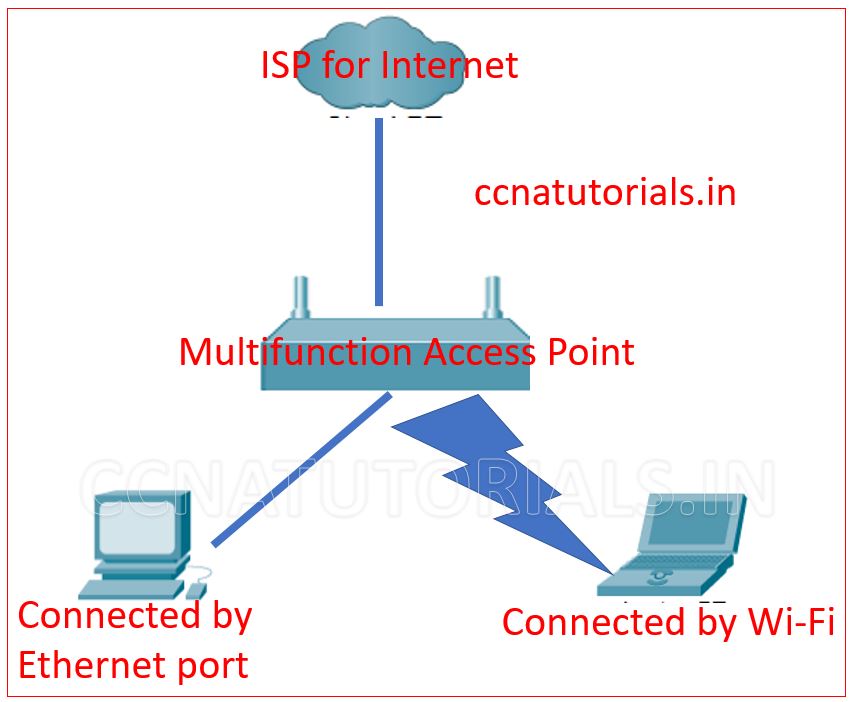
Multifunction access points are the combination of router, ordinary switch and a router. Router connect the local LAN with WAN or internet. The wireless access provide the connectivity to the devices on Wi-Fi. The switch connects the device with wired connection Ethernet ports. Router works like a gateway to internet for all the connected devices. So the multifunction access point provides different services to the connected devices.
Control Access Points in networking
The concept of control access points is different from the above two access points. Controlled access points controlled by a central unit which is known as WLC Wireless LAN Controller. A WLC control multiple controlled access points in a network. WLC defines the rule for each user. I mean which user can access from all users or from an individual user. The data flow from one device to another device is controlled by the WLC.
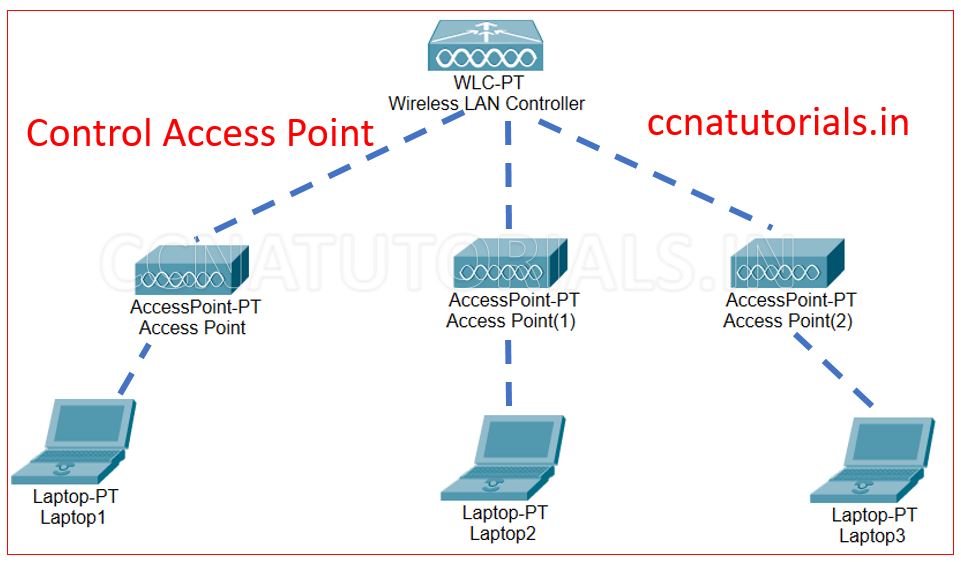
When a data packet received by a control access point, the access point send the information to the wireless LAN controller. The wireless LAN controller check the rules for particular user and allow the access point to transmit the data packet to its destination device.
In this article I describe some basic features of Access point in networking. I hope you found this article useful. We always happy to listen from our readers. You may drop a comment below or contact us on this topic. your suggestions are always welcome