In this article I describe the DSL Digital Subscriber Line in computer network for CCNA exam. PPP Point to Point Protocol is related to Link layer of TCP/IP Suite model. DSL Digital Subscriber Line provide the connectivity to the internet. DSL Digital Subscriber Line provides the high bandwidth communication on internet for data as well as for voice. The DSL Digital Subscriber Line is generally copper wire lines but in today scenario the copper wires replaced by the OFC. Generally the DSL Digital Subscriber Line allow to communicate with voice as well as with data. The variants of DSL are ADSL, HDSL etc. DSL Digital Subscriber Line works as a part of ISDN. ISDN is generally known as Integrated Services Digital Network. DSL Digital Subscriber Line provides by the telephone networks. The DSL Digital Subscriber Line generally works in the Mhz range of frequency for data and voice communication. The telephone network uses many multiplexer to provide the communication for public user. The resources are limited and the customers are unlimited so multiple services like multiplexing and ATM used to provide connectivity for public users.
Routing and Routed Protocols provides the connectivity between different networks for data packets flow from one network to another network. A standard routing table is maintained by the routers for data packet flow between different networks.
Before going to learn about DSL Digital Subscriber Line in computer network in detail, it became helpful to remember the OSI suite and TCP/IP suite model. There are many manufacturer of computer machine in the market. Initially when computers became single user public computer. The computers communicate with only same brand machines. It happens because there was no any fix standard for data transfer between different devices. It is very difficult to make communication with each other when the hardware are of different brands or company. In this article I describe the some basic part of OSI reference layer and TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts in networking with the DSL Digital Subscriber Line in computer network.
OSI reference model basic concepts
OSI reference model in computer network followed by various vendors to overcome the compatibility problem. After implementation of OSI reference model in computer network, equality maintains by all manufacturer. In 1970 the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model was created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The OSI model was meant to create inter-operable network with different manufactured devices. In this article I describe some layered approach of TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts in computer network. Before understanding the TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts it is necessary to know about the 7 layers of OSI reference model because the basic work of each layer is described in the OSI reference model. You can read the full article related to OSI reference model in computer networking here.
Importance of OSI reference model for DSL Digital Subscriber Line
Before going to know about the DSL Digital Subscriber Line at link layer. It is necessary to know the function of layers in OSI model and TCP/IP model. Initially not only hardware but software also not supported for work the different computer brand. It became very difficult for all computer users to working without implementation of OSI reference model in computer network. It is necessary then to make some common protocols for all vendors of computer. Before implementation of OSI reference model in computer network, all vendors implements their own protocols on computer hardware and software.
In networking OSI reference model became helpful. OSI reference model describes the flow of data between nodes in any network. Data from one computer application to another computer application transfer by following some common protocols. The OSI reference layer also become beneficial for troubleshooting the network problems. TCP/IP and Cisco three layered hierarchical model of Cisco became more helpful alongside the OSI reference model.
The Layered Approach in computer network
The Layered approach was the best way to make equality for all computer devices. Layers are not physical but following some protocols. Protocols are for connectivity, connections, data transfer and more. All manufacturer begin to follow the layered approach for OSI reference model in computer network. The OSI reference model change in TCP/IP reference model and later on Cisco three layered hierarchical model. OSI layer architecture have 7 layers. TCP/IP reference model convert these 7 layers into only four layers. After that Cisco three layered hierarchical model converts these 7 layers into three layers. Some layers combined to work in a single layer.
OSI is acronym for open system interconnection. The OSI is a logical reference OSI reference model in computer network. OSI model helps for data flow between different devices and operating systems. All manufacturer used their own architecture before invention of OSI reference model. It was very difficult to establish data communication between different devices. To overcome this problem international organization for standardization (ISO) created the open systems interconnection (OSI) reference model. OSI reference model make data flow possible between different operating system, devices and hardware. Later the OSI model adopted by Cisco as Cisco three layered hierarchical model.
Structure of OSI reference model related to DSL Digital Subscriber Line
OSI reference model in computer network consist of 7 layers. These 7 layers further divided into two groups. First 3 layers works for application communication and remaining 4 layers works for data flow. Application, presentation and session layers define the application communication. Transport, network, data link and physical layers define the data flow. Networking protocols works only on last four layers.
TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts for DSL Digital Subscriber Line
TCP/IP is acronym for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP suite model). In this section of the article I describe about TCP/IP suite model basic concepts in detail. TCP/IP suite model is a reference model like OSI layers. Instead of 7 layers of OSI reference model. TCP/IP suite model consist only four layer. All seven layers are merged into four layers only. TCP/IP suite model was designed and implemented by Department of Defence (DoD). TCP/IP developed to preserve data integrity. The main purpose to develop the TCP/IP is to provide security in the network. A lots of protocols works on each layer to provide a secure network.
It is necessary to understood the protocols used in TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts. IP addressing play an important role in TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts. By using the IP address and subnet masking broadcast domain breaks. It will improve the performance of the network. Breaking broadcast domain increase the data flow speed. Here IP stands for IPV4 only. We ignore the IPV6 for some time in this article. It will make it easy to understand the TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts.
A snap of TCP/IP Suite model basic concepts
In the decade of 1970’s TCP/IP suite model developed by DoD. In the initial stage TCP/IP suite model divided into two segments TCP and IP. Later its name registered with combined name of TCP and IP like TCP/IP model. ARPA, the Advanced Research Projects Agency of DoD officially authorised to use TCP/IP suite model. TCP/IP model was working well so it was adopted by many organisations. In today scenario it is mostly using reference model for networking. Internet is the best example of using TCP/IP.
Process or Application layer of DoD model in TCP/IP Suite model
This is the first layer of TCP/IP of DoD model. It is combination of top three layers of OSI reference model. The functions of Application layer, presentation layer and session layer in OSI model works in single layer process layer. This layer supports the point to point communication and controls the user interface. The data encryption and decryption also done at this layer. Example of some protocols functions at this layer are TLS Transport Layer Security, FTP, LPD, TFTP, SMTP.
Transport layer of DoD model in TCP/IP Suite model
Transport layer of TCP/IP is same as the Transport layer of OSI reference model. It supports the TCP and UDP protocol. This protocol converts the main data segment into packets and transport to the internet layer. The responsibility of Transport layer is to combine the segments and built the data. The data should be reconstruct in its real form. Transport layer is also responsible for creating end-to-end communication between sender and receiver. This layer ensure the delivery of segment in sequence at the receiving device. This property maintains the data integrity.
Internet layer of DoD model in TCP/IP Suite model
Internet layer of TCP/IP is similar to the network layer of OSI reference model. Routing protocols functions on Internet layer of TCP/IP model. Addressing and filtering of packets is main responsibility of Internet layer of TCP/IP model. This layer provides the transmission of packet in the whole network. Some example of protocols functions on internet layer are ICMP, ARP and IP.
Link layer of DoD model in TCP/IP Suite model
Link layer is the least layer of TCP/IP. Basically link layer is combination of data link and physical layer of OSI reference model. Link layer is also known as Network Access layer. It works on MAC address based data transmission. Link layer handles the frame and bits. It receive the bits and constructs frame from merging bits in a sequence. In case of any bit is missing this layer request to re transmit the bits. Ethernet, FDDI, WAP etc functions on this layer. There is no any preset specification for link layer. Link layer functions on any type of existing media.
DSL Digital Subscriber Line Explained in brief
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. The full form of DSL explains itself. A Digital line dedicated to a subscriber is known as DSL. DSL Digital Subscriber Line is a communication medium which supports both data and voice. Digital Subscriber Line transmit and receive the digital data over the telephone line. This is old technology, in today scenario ISDN and other internet connection replace the Digital Subscriber Line. The technology is same but enhanced the DSL. Now ADSL is mostly used instead of DSL. ADSL is stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. Both ADSL and DSL provides physical connectivity to any computer or device with internet or other online services.
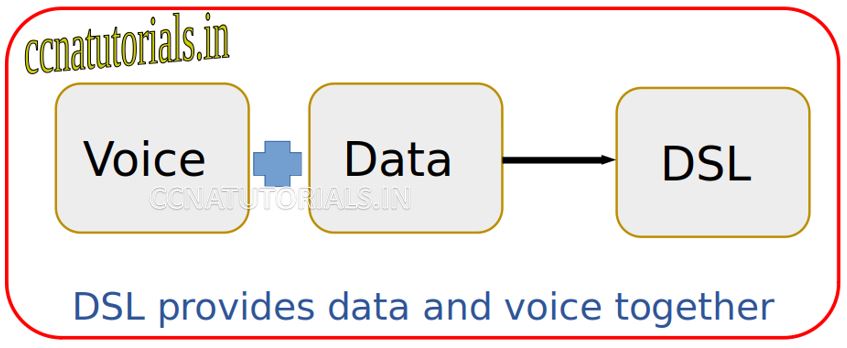
DSL provides both data and voice simultaneously on a single telephone line. A voice and data splitter used to separate the voice and data.
Function of DSL Digital Subscriber Line
DSL provides upto 100 Mbps speed to subscriber for data. The data streaming speed depends on many factors. The type of metal wire, condition of wire, equipment’s etc. Mostly ISP use this technology to provide the broadband data communication to its subscriber. Mostly DSL provides a constant speed which is available according to resources of ISP. Here ISP stands for Internet Service Provider. ISP provides connectivity to various services with subscribers.
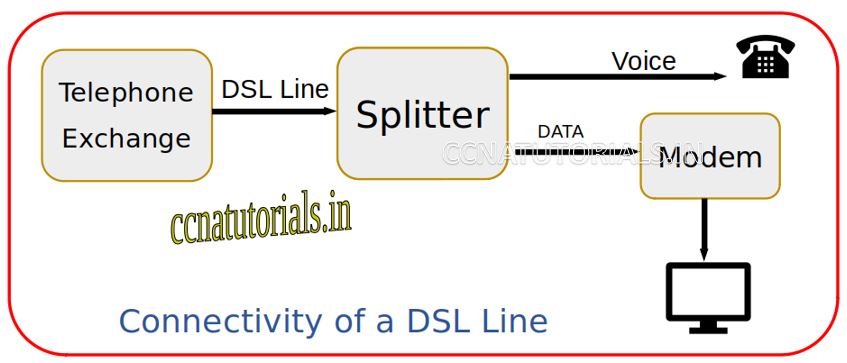
How Data and Voice travel together in DSL
Data and voice transfers simultaneously for subscriber by DSL line. How it works for both data and voice. There is a modem uses for data transmission and reception. Modem do modulation and demodulation the digital data with analog signal. A DSL spliter is uses to separate the voice and data frequency. The spliter is just a band pass filter which filter the voice and data and send them to separate ports. The port which give frequency spectrum for data connected with modem. The modem do modulation and demodulation of data from incoming signal.
Types of DSL The Digital Subscriber Line
DSL Digital Subscriber Line are of two types one is symmetric and another is asymmetric. Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line known as SDSL. SDSL provides the upstream and downstream equal speed. There is no variation in between the uploading and downloading speed via SDSL. Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line known as ADSL. ADSL commonly distributed to subscribers. The ADSL is differ from SDSL in the term of speed. The uploading and downloading speed of data are different. ADSL provides high downloading speed and low uploading speed. The common download speed is upto 20 Mbps and upload speed is maximum 2 Mbps.
DSL Digital Subscriber Line types
DSL Digital Subscriber Line provide the data and voice communication on a single line of copper wire. The line provide the analog signal but there is a device used to convert analog signal to digital signal known as MODEM. A data slitter used to separate the data and voice from incoming signal. DSL is of two types symmetric and asymmetric DSL. Generally Asymmetric DSL provided by the ISP. Which is known as ADSL. Symmetric DSL provides the same data flow speed for uploading and downloading stream on internet. The Asymmetric DSL works on different uploading and downloading data speed on internet.
Use of DSL Digital Subscriber Line
DSL Digital Subscriber Line is Cost Effective. DSL Digital Subscriber Line connection is very cheap and comfort for installation and use. The Internet Service Provider ISP keep the availability of DSL to provide publicly. A user can use the voice and data simultaneously with DSL connection.
In this article I describe the DSL Digital Subscriber Line in computer network for CCNA Eam. I hope you found this article helpful for any query or suggestions you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.







https://waterfallmagazine.com
Hi there, I enjoy reading all of your article post. I wanted to
write a little comment to support you.