In this article I describe Administrative Distance in IP routing related to networking for CCNA Exam. Administrative Distance in IP routing indicates the strength of connected router with an interface. We can say to manage the selection of best path for a data packet administrative distance in IP routing play a major role. Administrative Distance in IP routing provides a metric for selection the best path for data transfer from source to destination.
Administrative Distance in IP Routing is a logical term which are integer from 0 to 255. The strength of communication is decreases from 0 to 255. It means 0 is the best selection of path and 255 can not be used for data packet sending. Administrative Distance in IP routing number used by router according to the protocols available in routing table. All routing protocols have a default Administrative Distance in IP routing, but the network administrator can change these values for any particular reason. Administrative Distance in IP routing is not a long topic so alongside it will be beneficial to learn something about IP Routing process of routers.
The term IP Routing Process in router related to networking. IP Routing Process in router belongs to IP routing in router. IP Routing Process in router is a process of packet transfer between different networks via a router. When we access the internet or intranet the data packets transmitted and received by IP Routing Process in router.
Every interface of router has a different network. Routers are also known as layer3 device. Various routed and routing protocols used for moving packets between different networks. Generally the IP Routing Process in router is done by static routing, default routing and dynamic routing protocols.
Requirement of IP Routing Process in router
The function of a router is to move the data packets from one interface to another interface or we can say between different networks. The movement of packets done at layer 3 which is known as network layer of the OSI reference model. Router keep the information of neighbour router and network in its routing table.
There may be many interfaces in a router which connect different networks. How the router moves the packet to its destination it depends on routing and routed protocol. Static route in a router is a set of protocols which allow the router to transfer the packet to its destination. To understand the IP Routing Process in router it is necessary to know about the routing and routed protocol firstly.
Routing protocol for IP Routing Process in router
Routing protocols helps router to build and maintain the routing table in routers. Routing protocols are one important part of default routing in router. Routing protocols inform the router about the networks connected at each interface. Routing protocols doesn’t carry or push the data packets in any way. Any change in the network required to be update in the routing tables of all routers. This task is carried out by the routing protocols. Routing protocols help the routers to select the best path to exit the data packets.
Example of routing protocols are RIP, RIPv2, IGRP,OSPF etc. Routing protocols further divided into distance vector, link state and hybrid protocols. These all routing protocols update the routing table of all routers in the network. You can see the routing protocols by “show ip route” command in privilege command mode of router. Routing protocols are not responsible for data packet flow in any way. Routing protocols spread the information of network hierarchy to all routers.
Routed protocol for IP Routing Process in router
Routed protocol works with the data packets for default routing in router. Routed protocol sends the data packets within a router’s interfaces. Routing protocol decide the best path and routed protocol send the packets on these paths. Routed protocols are defined on interfaces of router. Routed protocols do not update or maintain the routing table in a router. Routed protocols are responsible for flow of data packets from one network to another network.
Routed protocols sends the data packets to correct exit interface of the router. Routed protocols are configured on interfaces of the router. Example of routed protocols are IP, IPv6, IPX and Appletalk. Routed protocols are basically addressing schema of the interfaces of router. Router identify the destination network of a data packet and send the data packet to correct exit interface. The concept of subnetting takes place in routed protocols.
Fundamentals of IP Routing Process in router
We know that routers used to connect the different LAN and WAN. We required to connect the different network with a router physically firstly. After completion of physical connectivity next step is to configure the logical network addresses and routing protocols. Each LAN or WAN works in a fix network ID. In case of router I mention the network ID for each LAN. When we work in a LAN, I mention the IP address for each host. Each host assigned a gateway which is the interface of the router to out the packet from that LAN. Router do not forward the packet to host. Router transfer the packet for network ID.
The flow of packets between different LAN depends on destination address on the packet. All routers maintain the routing table to determine the best route to remote network. Routing protocol keep update the routing table in IOS of router. The routing table help to find the destination network of a packet. Basically multiple protocols works for dynamic routing in router to transfer the data between different networks.

Function of routing table with administrative distance in IP Routing
Suppose a router get two different updates for the same remote network ID. Router require to add both updates in it’s routing table. But the router maintains a sequence to update routing table. Fist thing checked by the router is Administrative Distance. If the Administrative Distance of both updates are different, the lowest AD will be chosen and added in the routing table. If both updates have same Administrative Distance, then other metrics used to find the best path for the remote network. Other metrics are hop count, clock rate and band width etc. Again, the update with lowest metrics will updated in routing table. In case of equal metrics, the routing protocol will load balance for the remote network.
Table of default Administrative Distance in IP Routing
The below table show the Administrative Distance of different protocol and connection with router. Based on Administrative Distance, the best path for remote network is selected by the router. the values in below table are default values of Administrative Distances.
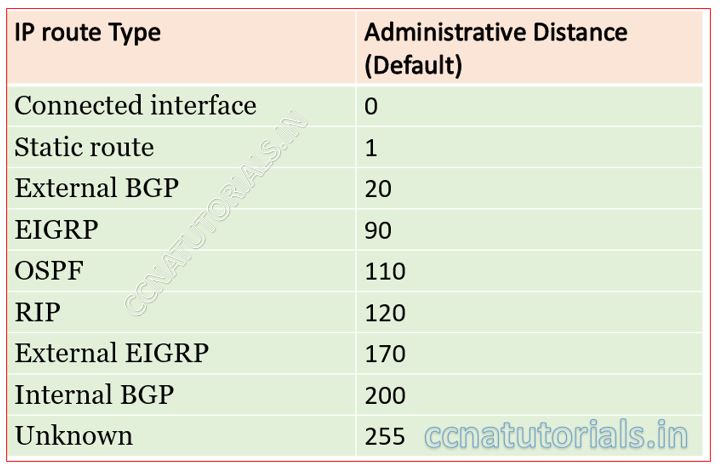
Meaning of Administrative Distance values
You can see the administrative value of direct connected network is 0. The most trusted link is directly connected network. Its value is fixed to 0. The router always selects the path of directly connected network. Static route has the value of Administrative Distance 1. After directly connected the second trusted path for remote network is static route interface. You can set the Administrative Distance of static route in routing table.
I believe you found this article helpful for your study of CCNA exam. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below. We always welcome the suggestions of our readers.







You made some really good points there. I checked on the internet for
more information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
thanks dear