In this article I describe the Routing Information Protocol in networking for CCNA Exam. Routing Information Protocol is a Distance vector routing protocol. We know the distance vector protocols are belongs to Dynamic Routing in router. We can configure the IP routing in router manually or dynamically. Static IP Routing in router perform the packets transfer very efficiently in small network. It is very difficult to configure and maintain the static IP Routing in router for large networks.
Routing Information Protocol is an Interior Gateway Protocol. RIP select the best path for data packets on the metric of Hop count. In a RIP enabled network, router share the connected network topology to neighbour routers. RIP can be used in small networks where maximum 15 routers are working for internetworking. In a RIP enabled network the routers maintained a routing table which store the information of all networks connected within the internetwork. I explain the distance vector routing protocols along with the Routing Information Protocol overview in this article.
We required an automatic method of routing in routers in large networks. So we use the dynamic routing in big networks one of them are distance vector routing protocols and other one is link state routing protocols. Basically routing is necessary to flow the data packets from one network to another network. We configure the routing table in routers to achieve the aim.
Distance vector routing protocols helps to select the path for data packets in network. Routers are self responsible to transmit the new update in routing tables. Dynamic routing protocols dynamically select the network distance and other factors for data flow in a large network. It will be helpful to know about the dynamic routing in router alongwith the Distance vector routing protocols.
Dynamic routing in router
Maintenance of routing table in all routers in a network is very critical job. Dynamic IP Routing in router make it easy to maintain the routing table in all routers in a network. Dynamic routing protocols make it easy to take decision to select the best path for data packets. The routers transmits and receive the routing information in a fix time interval and update the routing table.
Any change in network is immediately updated in all routers by sharing information. The drawback of dynamic routing is that more bandwidth consumed than static routing. Dynamic routing make easy to maintain the routers in large network. When a router gone defective or new router added in network, the dynamic protocols updates the routing table in all routers in network. The routers exchange the network update between each other by broadcasting and multicasting.
Example of Dynamic IP Routing in router
In static routing we configure the route in routers manually. Some dynamic routing protocols help to do the job of static routing in all routers in a large network. RIP (Routing information protocol) OSPF ( Open Shortest Path First) are examples of dynamic routing protocol. Dynamic routing protocols are further used two methods for sharing the routing information. Distance-vector and Link-State routing protocols used different technique for sharing route table information.
Distance vector routing protocols (RIP)
You can see there are two terms in DVRP. The first term is distance and second is vector. Distance is number of hop or step to sent the data packets up to destination network. Path selection for a data packet is depends on the hop count. Minimum hope count path selected by the Distance vector routing protocols. The term vector refers to the propagating of the packet on a given set of network nodes. Routers broadcast the information of remote network to next router. Every router do the same thing so the routing table of all routers updated automatically. All router inform about the connected networks to next router then router update its own routing table.
Network topology changes time to time. Adding or removing a router in a network is very common phenomena. Any change in network should be updated in all router’s routing table. Doing this manually is very critical work. Distance vector routing protocols do this job automatically. The process of broadcasting any update in routing table and updation in all routing tables is known as convergence.
Function of Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
RIP advertise the connected network is to neighbour routers. All RIP enable router do this on a fix time interval. By sharing and updating all network id in routing table. All routers know about the different networks in internetwork. Routing information protocol helps router to select the best path for data packets. RIP is a pure distance vector routing protocol. On receiving multiple requests for same destination network of data packets RIP decided on hop count. The route which have minimum hop count is selected on priority. The algorithm used by RIP for select best path for data packet routing is known as Bellman-Ford algorithm. Hop count is metric which is preferred by RIP enabled network devices.

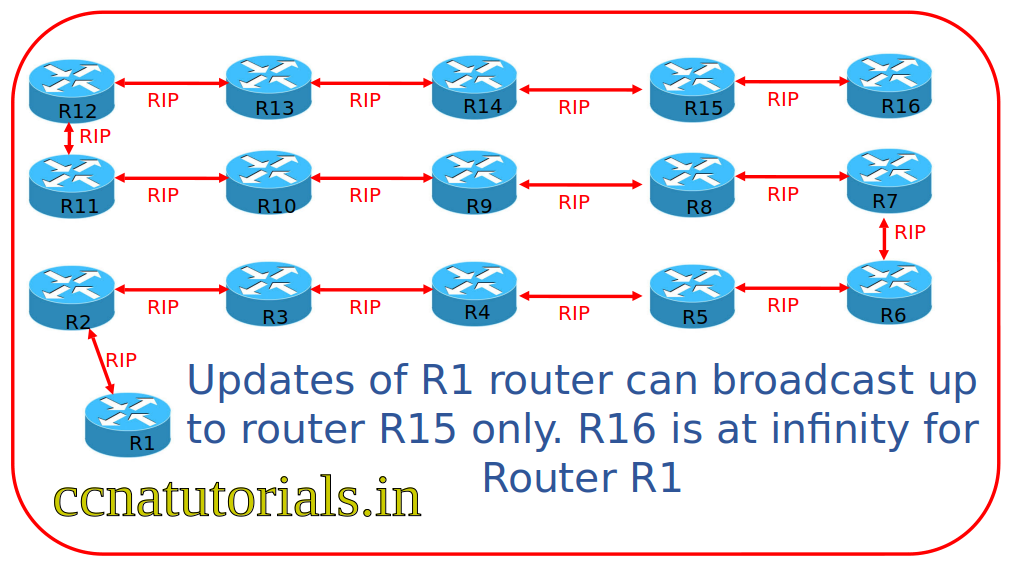
RIP version 1 generally known as RIP is supports only classfull network schema. While RIP version 2 supports the classless network schema also. RIP use UDP port 520 for advertisement the routing table of a router. RIP supports maximum 15 for destination network. The 16th hop supposed as infinity hop.
Routing Information Protocol technical term explained
RIP version 1 generally known as RIP is supports only classfull network schema. While RIP version 2 supports the classless network schema also. RIP use UDP port 520 for advertisement the routing information on network. RIP supports maximum 15 hop(16 infinity) for destination network. The 16th hop supposed as infinity hop. All RIP response packets broadcast every 30 seconds. If any update failed to get up to 180 second, the entry removed automatically. 180 second is invalid time for RIP broadcast packets.

Routing Information Protocol Messages
Routing information protocol used only two types message. First is request RIP message and second is RIP response message. You can understand the message type by its name. A RIP request message broadcast to check any new change in the network. RIP request message also sends by a router when the RIP enabled router to come online. On request RIP message all routers reply with RIP response message so the requisite router can update the routing table.
Versions of Routing Information Protocol
Routing Information Protocol is of three types RIP, RIPv2 and RIPng. RIP is also known as RIPv1 which is first version of RIP family. RIPv1 do not supports the class less network schema. To check the RIP status, you can use the command debug ip rip in privilege command mode. To overcome the drawback of classfull network schema RIPv2 invented by IETF. RIPv2 supports VLSM (variable Length Subnet Mask). RIPv2 announce the routes by multicasting on 224.0.0.9 IP address while RIPv1 broadcast the routing table on 255.255.255.0. The RIPv2 has another feature that summarize the network addresses. RIPng is the latest version with some advance features.
I provide the Routing Information Protocol overview in this article. I hope you found this article helpful. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.




