In this article I describe the method to Configure Access and Trunk mode VLAN. VLAN provides multiple virtual networks in a physical network. We can break a local area network into multiple virtual networks. The devices of same virtual network can communicate with each other without interfere to other virtual network. The switchports of a switch can be used as access port or trunk port. The function of access port and trunk port are different. before Configure Access and Trunk mode lets see some other related terms to VLAN.
The switch provide a single broadcast domain to all connected devices by default. Each port of switch creates single collision domain. VLAN breaks the broadcast domain into small broadcast domain. If we need to make communication between different VLANs then we need a router. Router have the feature to provide communication between different networks. VLAN provides the logical network within a single physical network.
VLAN basic concepts to Configure Access and Trunk mode
Every switchport works on separate collision domain. We can say each device connected with a switchport remains in separate collision domain. By default all switchports of a switch works in a single broadcast domain. It can be define as all the devices working in a single LAN remains in a single broadcast domain. The big network of single broadcast domain can be divided into different small broadcast domains by creating the VLANs in the network. Every VLAN have its own broadcast domain.
Breaking the large broadcast domain into small broadcast domains provides an extra layer of security in the network. The devices of different broadcast domains can not communicate with each other. The swithports can be configured to restrict the unauthorised use by unwanted devices. Management of networking devices become easier by creating VLANs. Network administrator can monitor the small network more efficiently than a large network.
Methods of adding devices in VLAN
The devices can be added in a VLAN by two methods static and dynamic. Actually we configure the switchports for access by device with these methods. Generally static method assigned to the VLANs as it is easy and secure method. In static method we add the switchports manually to a VLAN. Suppose I assign the switchport number 4 to VLAN 10. This switchport remains assigned to VLAN unless we manually change it or assign to another VLAN. By default all switchports assigned to a single VLAN. We need to assign each port manually to the required VLAN.
The other method is dynamic assignment of swithports to VLAN according to the IP address of a device or MAC address of the device. Suppose a device connected to switchport 2 and it belongs to VLAN 20. If you change the switchport of this device from 2 to 10 then the switchport 10 automatically assigned to VLAN 20 and the device will work as it was. Dynamic method works in high end switches, in normal switch we can use static methods only.
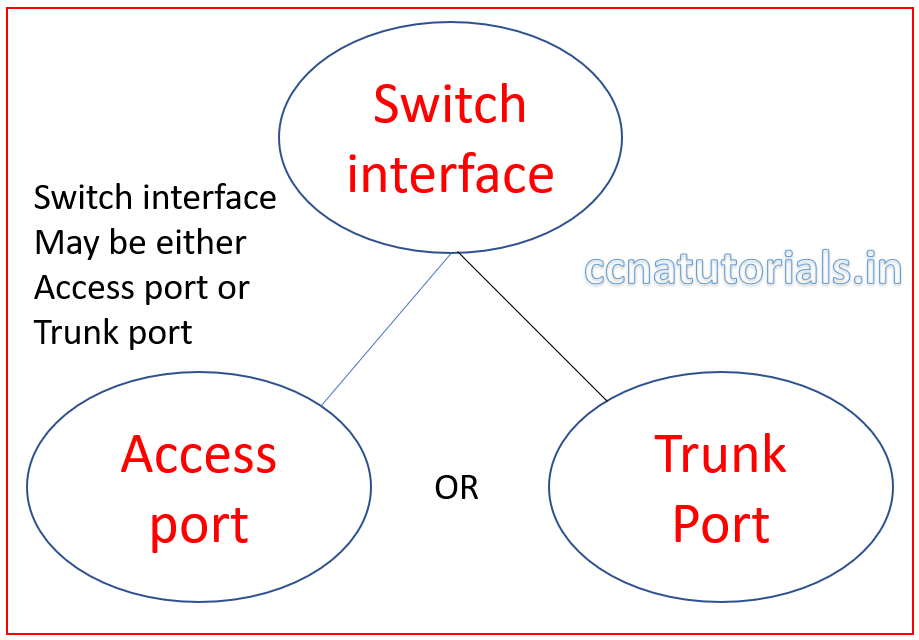
Access port and Trunk port for VLAN
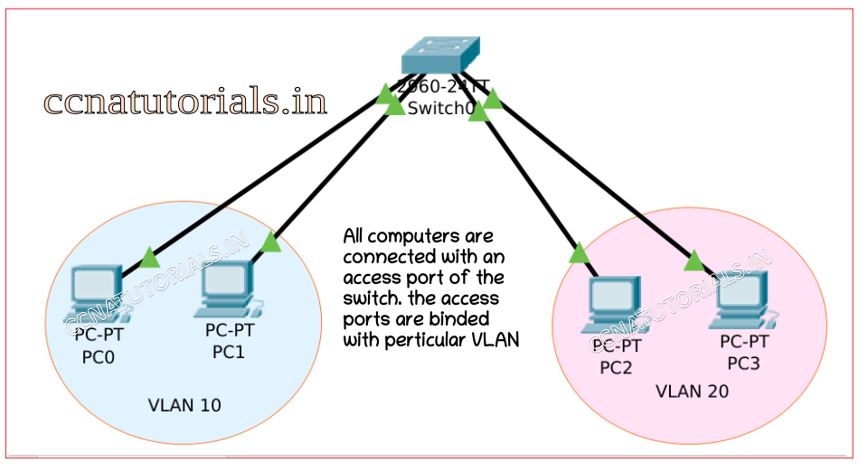
Access ports allow a device to access the network by using the NIC or RJ45 connection. The devices connected to access ports remains in same broadcast domain. The device can access, receive and transmit the data via access port. Generally all switchports remains as access ports until we manually convert them to trunk ports.
Trunk port mode allow to transmit and receive the data of multiple VLANs. Generally endpoint devices not connected with trunk ports. The networking devices uses trunk ports to connect with each other. For example when we need to connect two switches which have multiple VLANs, the switches can be connected via trunk ports. The assignment of access ports and trunk ports are logical. A switchport mode can be changed by using the command line interface.
Access and Trunk ports belongs to Layer 3 switch. Function of Access and Trunk ports are different. According to name of ports access ports provide facility to flow the data packets through it. Trunk ports allow to pass the traffic of multiple VLANs through it. Access and Trunk ports play an important role for creating VLANs in a LAN.
VLAN created on access ports in a layer 3 switch. Trunk ports provides connectivity between VLAN to VLAN from one switch to another switch. In this article we discuss only of basic of access and trunk ports. A switch-port can be assigned either access port of trunk port. It is not possible to assign both properties access and trunk ports to a single port.
Access ports of a Later 3 switch
Access port belongs to a particular VLAN. By default, all access ports of a switch remain in a VLAN 1. It means any device connected with any access port can communicate with another device. The condition is that all devices should have a same subnet mask. If all devices have same subnet mask, it means all devices belongs to same network ID can communicate with each other. Access ports receive and transmit the data for the same VLAN. The access port doesn’t check for source address on data packets.
VLAN works as a separate broadcast domain in a LAN. You can say if there are 5 VLANs in a LAN, there are 5 broadcast domains lying in the LAN. Each device belongs to VLAN assume in separate broadcast domain. The access ports in a VLAN works like separate collision domain for the connected device. Devices of different VLAN can communicate by configuring inter-VLAN routing with the help of a router.
Trunk Ports of a Layer 3 switch
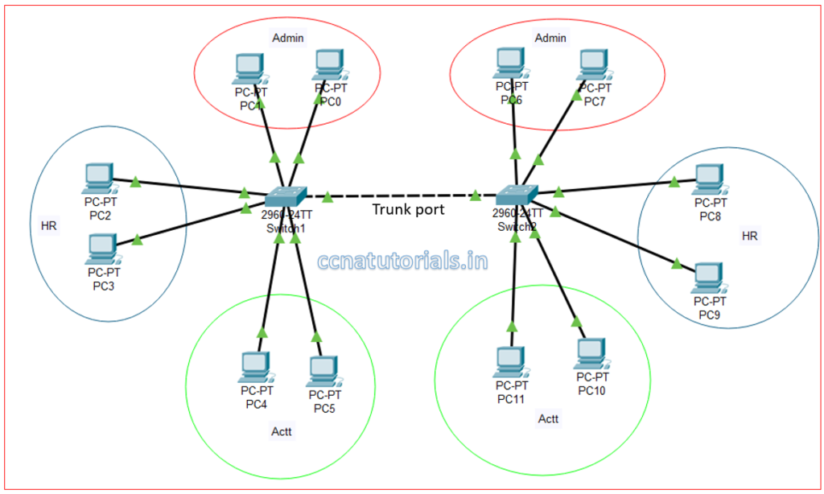
Trunk ports are not separate ports on a layer 3 switch. Any interface can be defined as Access or Trunk port. The task of trunk port is to carry the data of all VLANs available in the whole switch interfaces. I mean to say suppose you have 4 VLANs in a switch and want to carry all 4 VLANs data to another switch via a single port. In this case you must assign a single port as trunk port in that switch.
Similarly, in another switch a single port also assigned trunk port. Both switches should be connected with the trunk port to make communication between all VLANs of different switches. A trunk port can carry the data of all VLANs together for another trunk port. We can say just like a telephone line which can carry multiple voice calls without disturbing each other. The trunk port can carry multiple VLANs data without interfering each other in a network. A trunk link speed is 100, 1000 or 10000 Mbps point to point link between two switches.
The router works like a gateway between the VLANs. One access port can be assigned to a single VLAN only. It is not possible to assign two VLANs to a single access port. For data transfer only single VLAN can be accessed by an access port. When you are working with voice and data transfer via a single access port. You can assign a data VLAN and a voice VLAN to a single access port. But the rule is that only single VLAN of same pattern can be assigned to an access port.
Configure Access and Trunk mode
A switch port can configure access and trunk mode by some simple commands. Remember the basic functionality of access and trunk mode of a switch port. Access mode port can receive the data of same VLAN tag and transmit the data within the same VLAN. Trunk mode port connects different switch.
A trunk mode port can carry the data of multiple VLAN through it. At the end the trunk mode port distribute the data packets to related VLAN ID. Access mode port works like a single line phone. Trunk mode port works like a carrier for multiple telephone lines. The identification method in access and trunk mode port is frame tagging on packet with VLAN Id.
In this article I discuss to configure access and trunk mode of a switch port. There are simple command to configure access and trunk mode to a switchport.
Configure access mode to a port of switch
All switch ports remains in single VLAN 1 and in access mode.by default. Once you change the switch port to trunk mode the default property of switch port vanish. To get back a switch port from trunk mode to access mode you need to run the below command from global command mode of CLI. Suppose we need to change the mode of FastEthernet 0/1 to access mode.
Switch>en Switch#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] Switch(config)# Switch#
Similarly we can change the mode of any switch port. It is not necessary the switch port must be fastethernet port. Any interface port of switch can be changed to access mode. It may be GigabitEthernet also.
Configure Trunk mode to a port of switch
We know by default all ports of a switch remain in access mode. We want to send the data from one VLAN to same VLAN on other switch than we need to configure a switch port to trunk mode. Trunk mode port can receive and transmit the data of multiple VLANs via a single media. The trunk port may be any FastEthernet port of GigabitEthernet port. The commands are same as we discuss above. Here I am going to change the mode of switchport GigabitEthernet 0/1 port to trunk mode. Remember one thing once you changed the mode of any switch port do not connect any VLAN device with it. The trunk mode port does not belong to any VLAN. It carry the data of all VLANs together. So see the below commands to change the mode of GigabitEthernet port 0/1
Switch>en Switch#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] Switch(config)# Switch#
Now the GigabitEthernet 0/1 port will behave like a tunnel for all VLANs to carry the data from one switch to another connected switch via trunk ports. You can set the speed of link and duplex mode for the trunk switch port.
Checking the mode of a switchport
You can check the mode of a particular switch port or all ports at once. By running the “show interfaces” you can see the status of all interfaces. But i need to check only trunk ports of the switch then i will run the following command.
Switch#show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/1 1-1005 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 1 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 1
In above command window you can see the first result of command “show interfaces trunk”. The status of Fa0/1 is trunk. If you have multiple trunk ports than this command will show all trunk ports status.
In this article I describe the method to configure access and trunk port for VLAN. For any query or suggestion on this article you may contact us or drop a comment below. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.







I am impressed with this site, very I am a big fan .