In this article I describe the Classes of IP address in TCP/IP model in computer networking FOR CCNA 200-301. Classes of IP address in TCP/IP model is the identity of any device in the network. Without IP address any device cannot communicate with the network or other devices. IP is acronym of Internet Protocol. In any network the devices are identify by its unique IP address. IP addresses further divided into different IP address Classes.
IP protocol works on internet layer in TCP/IP model. Classes of IP address system created by fix length binary numbers. The Classes of IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking is a logical numeric address allotted to devices in the network. MAC address is the hardware address and never change in any network.
The IP address can be changes for each device in a network. Classes of IP address in TCP/IP model was designed to allow hosts to communication with each other. IP system is the identity of any hardware device for communication in the network. The IP address system is of two types IPV4 and IPV6. Here in this article we discuss about IPV4 only. There is a separate article for IPV6 on this website, you can see it here.
Terminology of IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
Before going to explain IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking. Some terms are necessary to know which are used in IP address system in computer networking. A Bit may be either 0 or 1. One Byte is equal to 8 bits. One Octat is equal to 8 bits and. Network Address is the designation used in routing protocols for sending the data. It is basically the first address of any subnet.
Network address never used by any device. Network address is the identity of any network. Broadcast Address is used to send data to all nodes in a network. Broadcast address is the last IP of any subnet. In any network address and Broadcast address never assigned to any device. For example 192.168.1.3/24 IP belongs to Network ID 192.168.1.0/24 and Broadcast ID is 192.168.1.255/24.
Network Id is the IP address which use to identify the network. The first IP address of a block of IP address is known as network Id. The last IP address of the IP block is known as broadcast ID. For example 192.168.1.3/24 IP belongs to Network ID 192.168.1.0/24 and Broadcast ID is 192.168.1.255/24.
IP is acronym of Internet Protocol. In any network the devices are identify by its unique IP address. IP protocol works on internet layer in TCP/IP model. IP address system created by fix length binary numbers. The IP system is a logical numeric address. MAC address is the hardware address and never change in any network. The IP changes for each device in a network. IP system was designed to allow hosts to communication with each other. IP system is the identity of any hardware device for communication. The IP system is of two types IPV4 and IPV6. Here in this article we discuss about IPV4 only. There is a separate article for IPV6 on this website.
Designing of IP address system
An IP is combination of 32 bits. Each bit either 0 or 1 but not blank. 32 bits further divided into four Octate. IP can be written in two formats Binary or Decimal. Computer change the decimal into binary during communication. Example of IP in decimal is 10.0.0.0 same in binary 00001010.00000000.00000000.00000000 . User not used the IP in binary system. It is not easy to remember a 32 bit long binary number. During configuration in devices or routing we use the decimal format of IP . Some times IP is also written in Hexadecimal. We discuss about decimal and binary format in this article.
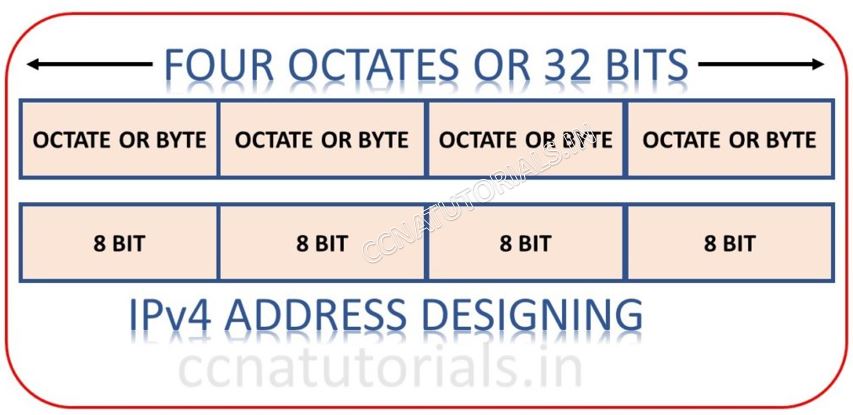
Structure of IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
We have approx 232 IP by using 32 bit binary IP which is equal to 4.29 billion approx. These are sufficient to provide connectivity to devices worldwide. We got sufficient IP to use but the problem is that how a Router can store 4.29 billion address in its routing table.
If each router in world keep these all address in it then the data flow speed become very slow. To overcome this problem IP is further divided into network and host part. Subnetting is come to picture to avoid this problem. Class or IP defines by dividing the IP into network and host segments.
In four bytes we can fix either first octate for network or first two octate or first three octate. IP class is also defining by the network bits. It is depends on your network how many hosts you want to join in the network. For small number of network and large number of host class A network created. For large number of networks and small numbers of host class C network created.
Network Addressing for IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
In any IP some bits keep fix to define network address. Remain bits are changeable and used for Host. For example in IP 192.168.1.0/24 first three byte remain same for each device in this network. 192.168.1 remains unchanged 192.168.1.0 is the Network Id and 192.168.1.255 is broadcast address. There can be 252 devices connects in this network. 252 devices can use the IP addresses from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254.
In four bytes we can fix either first Octate for network or first two Octate or first three Octate. IP Class is also defining by the network bits. It is depends on your network how many hosts you want to join in the network. For small number of network and large number of host Class A network created. For large number of networks and small numbers of host class C network created.
Broadcast Addressing for IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
In any IP some bits keep fix to define Broadcast address. Remain bits are changeable and used for Host. For example in IP 192.168.1.0/24 first three byte remain same for each device in this network. 192.168.1 remains unchanged 192.168.1.255 is the broadcast address. There can be 252 devices connects in this network. 252 devices can use the IP addresses from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254.
Public IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
Public IP address are those address which are used by internetwork devices for routing protocol. The public IP address are allotted by the ISP of special requirement. When we take an internet connection the ISP allot us only a single public IP which works like a gateway for our small network. Let’s take an example of our home network.
There is a single gateway allotted to us by the ISP in the modem. Behind the modem we are using multiple devices to access the internet. When we add a new device we never ask to ISP to allot a new IP address.
So the scene is that we always working with private IP address in our local network behind a single public IP address. Now let’s move on the topic related to private IP address in computer networking.
Private IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking
Private IP address system in TCP/IP model in computer networking are a slot of IP address which allow any organisation to create their own private network. These private networks are purely creates for the related organisation for personal use. A single group of IP address can be used by many organisations simultaneously. This is possible because the private IP address series does not configure in any routing table in all over the world. So the routing devices does not identify the devices which are using the private IP address in computer networking.
Class A address in IP system
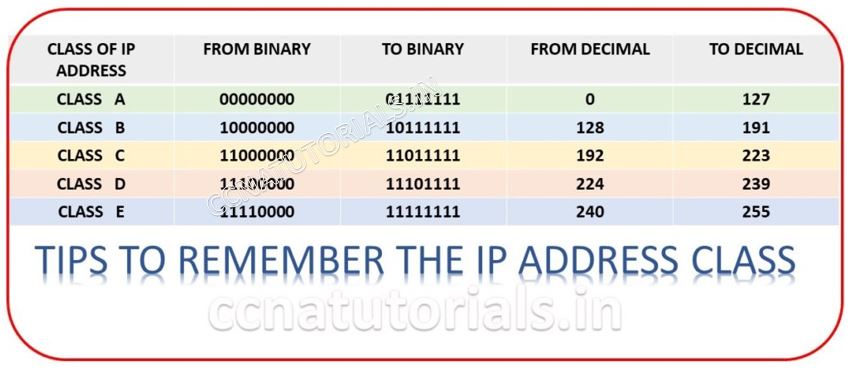
IP address is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class A network the very first bit remains unchanged and should be 0. All remains 31 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 0xxxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class A in IP system is from 00000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 011111111.11111111.11111111.1111110 in decimal it denotes 0.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses thats why 1.0.0.0 and 127.255.255.255 exempted in Class A in IP system. Because they are reserve addresses as discussed earlier.
Class B address in IP system
IP is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class B network the first bit remains 1 and second bit remains 0 of first octate. All remains 30 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 10xxxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class B in IP system is from 10000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 101111111.11111111.11111111.1111110 in decimal it denotes 128.0.0.1 to 191.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses thats why 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.255.255 exempted in Class B address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class C address in IP system
IP is a combination of 32 binary bits. In Class C network the first 2 bits remains 1 and third bit remains 0 of first octate. All remains 29 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 110xxxxxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class C address in IP system is from 11000000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11011111.11111111.11111111.1111110 in decimal it denotes 192.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses thats why 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255 exempted in Class B address in IP s system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class D address in IP address system
Class D addresses are reserve for research purpose. In symmerty to above address classes.In Class D network the first 3 bits remains 1 and fourth bit remains 0 of first octate. All remains 28 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 1110xxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class D in IP system is from 11100000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11101111.11111111.11111111.1111110 in decimal it denotes 224.0.0.1 to 239.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast address consume two IP addresses thats why 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255 exempted in Class D address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
Class E address in IP address system
Class E addresses are reserve for research purpose. In symmerty to above address classes. In Class E network the first 4 bits remains 1 of first octate. All remains 28 bits can be changed for assigning IP to host. The first octate looks like 1111xxxx where x can be 0 or 1. So the range or Class E in IP address system is from 11110000.00000000.00000000.00000001 to 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111110 in decimal it denotes 240.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.254. Remember Network ID and Broadcast addresses consume two IP addresses thats why 240.0.0.0 and 254.255.255.255 exempted in Class D address in IP system. Because they are reserve IP addresses.
In this article I describe the Classes of IP address in computer network for CCNA Eam. I hope you found this article helpful for any query or suggestions you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.






Howdy, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i
was just curious if you get a lot of spam remarks?
If so how do you stop it, any plugin or anything you can recommend?
I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any support is very much appreciated.