In this article I describe the Loop avoidance mechanism in RIP protocol in networking. Loop avoidance mechanism in RIP is necessary to avoid loop occurring in the network. Routing loops in distance vector protocols is a general phenomena. We know the RIP advertise the routing table after every 30 seconds. Routing loops occurs when the same information broadcast again and again from different paths in a network. To prevent these loops occurs there is some loop avoidance mechanism in RIP available.
Routing Information Protocol RIP
RIP version 1 generally known as RIP is supports only classfull network schema. While RIP version 2 supports the classless network schema also. RIP use UDP port 520 for advertisement the routing information on network. Routing Information Protocol RIPv2 supports maximum 15 hop(16 infinity) for destination network. The 16th hop supposed as infinity hop. All RIP response packets broadcast every 30 seconds. If any update failed to get up to 180 second, the entry removed automatically. 180 second is invalid time for RIP broadcast packets.
Routing Information Protocol RIPv2 advertise the connected network is to neighbour routers. All RIP enable router do this on a fix time interval. By sharing and updating all network id in routing table. All routers know about the different networks in internetwork. Routing information protocol helps router to select the best path for data packets. RIP is a pure distance vector protocol. On receiving multiple requests for same destination network of data packets RIP decided on hop count. The route which have minimum hop count is selected on priority. The algorithm used by RIP for select best path for data packet routing is known as Bellman-Ford algorithm. Hop count is metric which is preferred by RIP enabled network devices.
Routing Information Protocol Messages
Routing information protocol used only two types message. First is request RIP message and second is RIP response message. You can understand the message type by its name. a RIP request message broadcast to check any new change in the network. RIP request message also sends by a router when the RIP enabled router to come online. On request RIP message all routers reply with RIP response message so the requisite router can update the routing table.
Versions of Routing Information Protocol
Routing Information Protocol is of three types RIP, RIPv2 and RIPng. RIP is also known as RIPv1 which is first version of RIP family. RIPv1 do not supports the class less network schema. To check the RIP status, you can use the command “debug ip rip” in privilege command mode. To overcome the drawback of classfull network schema RIPv2 invented by IETF. RIPv2 supports VLSM (variable Length Subnet Mask). RIPv2 announce the routes by multicasting on 224.0.0.9 IP address while RIPv1 broadcast the routing table on 255.255.255.0. RIPv2 has another feature that summarise the network addresses. RIPng is the latest version with some advance features.
Loop avoidance mechanism in RIP
The routing loops in distance vector protocols divided in many kinds. Here in this article I describe the routing loops occurs in routing information protocol RIP only. I describe the reason of various kind of routing loops in distance vector protocols in this article. The routing loops are of 3 types in RIP distance vector protocol split horizon, Route poisoning and hold-down timer. So lets discuss in details about these terms.
Split Horizon loop avoidance mechanism in RIP
Split horizon loop avoidance mechanism in RIP is most useful feature to prevent the routing loops of Routing Information Protocol (RIP). The Split horizon prevents to advertise the same route to the originating router. I mean split horizon feature stop a router to send the update to the router from where it gets the update. Imagine a network topology as shown in figure below.
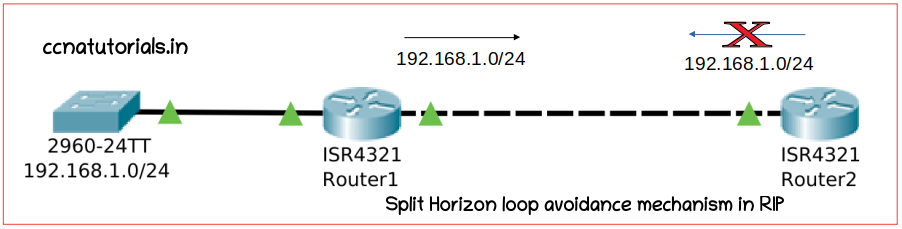
Router1 connected with a network 192.168.1.0/24 on one interface. Router1 advertise about the network 192.168.1.0/24 to Router2. On receiving update of the network 192.168.1.0/24 Router2 update its routing table. After 30 second Router2 broadcast the routing table to every nearby router. Router1 is also one of the neighbour or Router2. What is Router2 send the update about 192.168.1.0/24 to Router1? Router1 and Router2 broadcast the same network again and again to each other.
In this condition a loop generate between Router1 and Router2. Split horizon prevent this type looping in the network. Router2 knows that the network 192.168.1.0/24 broadcast by Router1 earlier so Router2 dont send this update to Router1. In this example I take only 2 routers think if there are 15 routers and each router broadcast the update back to originating router. The network will be chock very soon. So split horizon is most important loop prevention system for RIP enabled network.
Route Poisoning loop avoidance mechanism in RIP
Route poisoning for routing loops in distance vector protocols is a must necessary loop prevention system. We know that in RIP enabled network all routers broadcast the network connected with it. It will take some time for repetition about 30 seconds. Consider the scenario when a network connected to a router fails for any reason. In this condition the effective router needs to send a request to all routers that a network failed connected to it. If this information is not passes other network will not stop to send the packet for failed network. Consider the scenario as shown in picture below
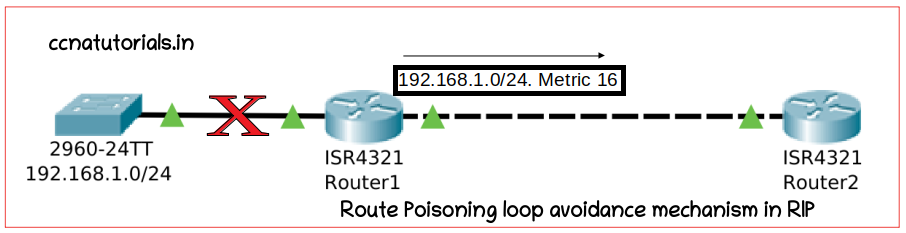
In this scenario Router1 connected with a network 192.168.1.0/24 at interface G0. Router1 continuously broadcast about the network 192.168.1.0/24 to Router2 and Router 2 further to other routers connected to it except Router1. Suddenly network 192.168.1.0/24 disconnected due to any reason. Only Router1 know this event but other Routers doesn’t know about it. Router1 immediately broadcast a RIP message to Router2 the the network 192.168.1.0/24 with metric 16.
We know RIP supports only 15 hop in a network. When Router2 got the information of network 192.168.1.0/24 with metric 16. Router2 repeat the same update to next router and next to next like a chain of updates. All routers come to know that network 192.168.1.0/24 have metric 16 and should be considered as infinite network. I hope you understand the route poisoning prevention of RIP enabled network.
Hold Down Timer loop avoidance mechanism in RIP
In previous prevention system Route Poisoning we learn that a router inform to all RIP enabled network about a failed network with metric 16. Hold down timer is depends on route poisoning prevention. Actually what is happening now see in detail. When Router 2 gots an update for a network with metric 16 from Router1, Router2 put the metric 16 network in hold time. Hold time is 180 seconds in RIP. This hold time remains until the Router1 send an update about the failed network status without metric 16 to Router2. So we can say hold time allow a router to keep a network in its routing table but it is considered as infinite network until the originator Router send an update that the network is live again.
So above three loop prevention techniques are used for RIP in a network. I hope you understand these loop prevention system. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below.





This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.