Contents of this article
In this article I describe the OSPF Multi Area network. Routing protocols helps router to build and maintain the routing table in routers. Routing protocols are one important part of default routing in router. Routing protocols inform the router about the networks connected at each interface. Routing protocols doesn’t carry or push the data packets in any way. Any change in the network required to be update in the routing tables of all routers. This task is carried out by the routing protocols. Routing protocols help the routers to select the best path to exit the data packets.
Example of routing protocols are RIP, RIPv2, IGRP, OSPF etc. Routing protocols further divided into distance vector, link state and hybrid protocols. These all routing protocols update the routing table of all routers in the network. You can see the routing protocols by “show ip route” command in privilege command mode of router. Routing protocols are not responsible for data packet flow in any way. Routing protocols spread the information of network hierarchy to all routers.
We know the OSPF works on Area ID. Before going to this chapter I hope you aware about configuration of OSPF in single area. What is the need of multi area if we can use routing in single area? The question is sound good.
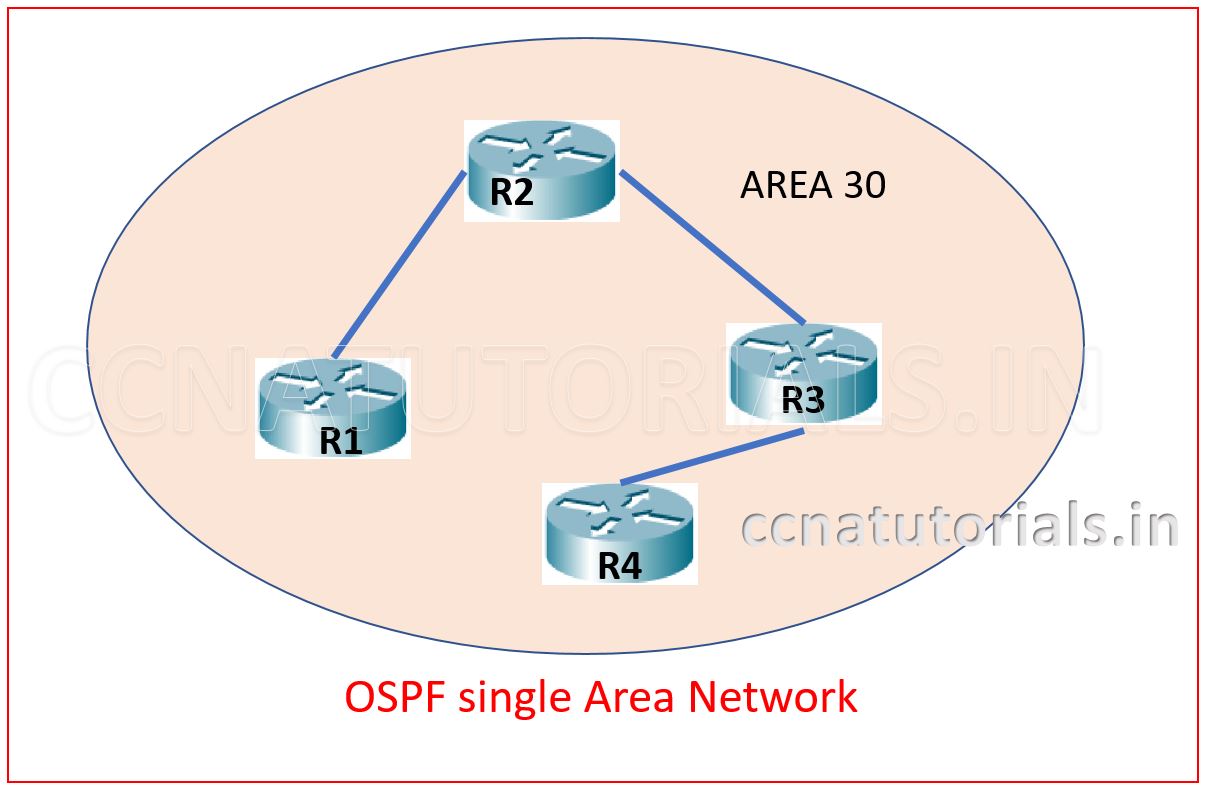
The basic reason for breaking the single area in to multi area is maintenance of network. We know the advantages of OSPF over the RIP and EIGRP protocols. OSPF is a link state routing protocol and RIP is distance vector protocol. The performance of any network depends on the convergence time of the networking devices. The minimum convergence time provides good data transfer speed in a network. Let’s discuss about the OSPF Multi Area network.
Reason behind using OSPF multi area network
In link state routing protocol the database of each router updated periodically. We need to reduce the updates so the convergence time reduced. Since router update its database each time when the network topology changed. So if there are a lots of router in a single area then they will also have a lots number of links. Every time when a link is down or changes state each router in the same area required update its database. These updates broadcast by LSA (Link State Advertisement) packet advertisements. It will take more time to convergence in a single area for a lots of router in it.
When we break an area into multi area, the number of routers reduced. So the numbers of links also reduced. We know the router update database for own area ID only. By breaking the area the convergence time reduced. So the large single area OSPF suffer from some serious challenges. Hence OSPF move towards the OSPF multi area network concept in place of single area.
OSPF multi area network explained
See the image below this paragraph. The image showing routers divided into three different Area ID. The router advertise the updates within its own Area ID.
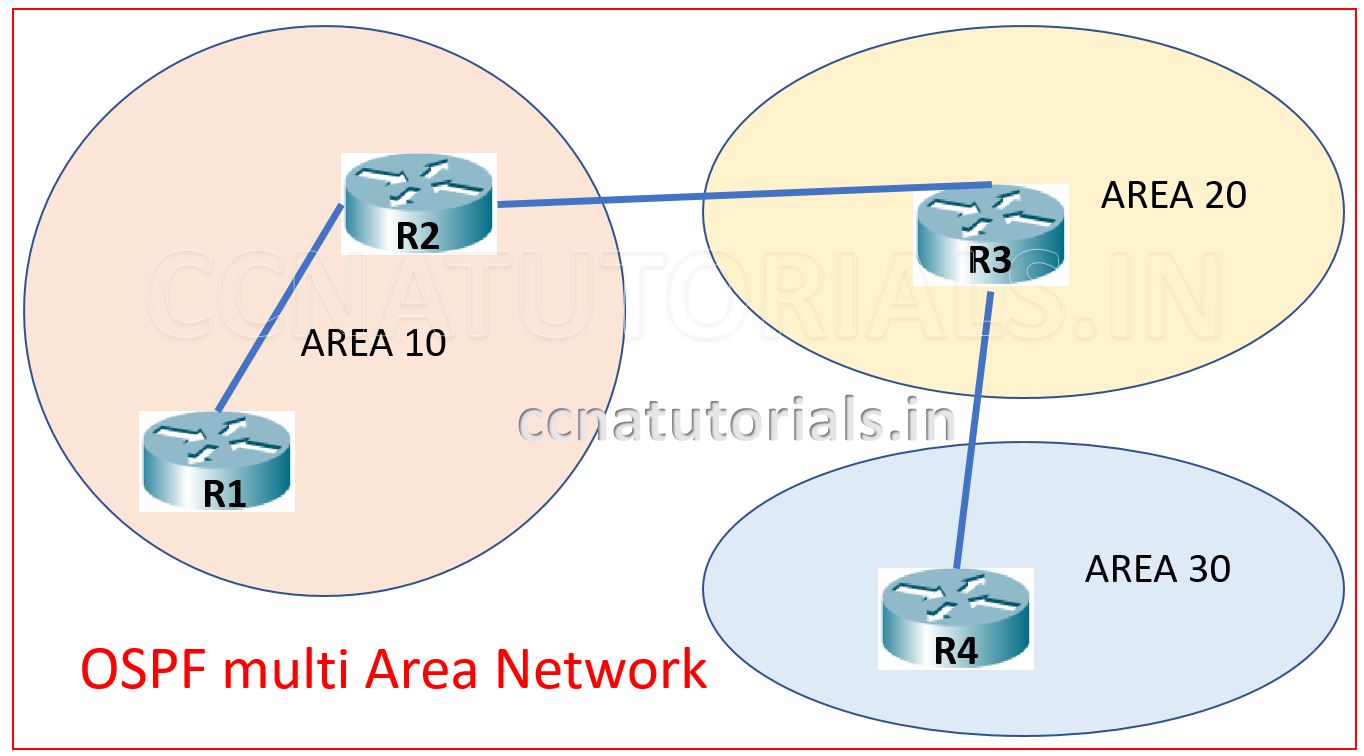
After breaking the single area into multi area the router belongs to any area do not require to update database for entire network. This feature or router reduce the memory overload and convergence time. Another main effect of multi area is that changes in topology of any area do not effect to the whole network. The configuration of OSPF multi area network is little bit complex than the single area OSPF configuration.
Types of router in OSPF multi area network
The router defined by the role or routers in OSPF multi area network. Some routers remain in a single area, some remains on border of two areas etc. so the routers are defined as backbone routers, internal routers, border routers and autonomous system boundary routers. See the below image in which various router defined.
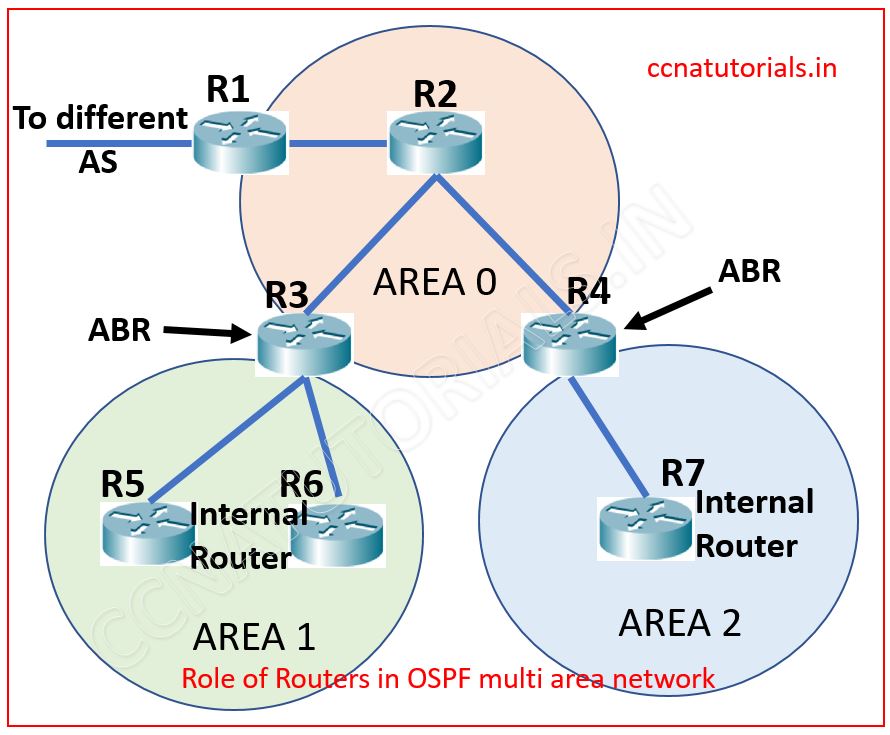
In above image router R1, R2, R3 and R4 belongs to Area 0. R5 and R6 belongs to Area 1 and R7 belongs to Area2. Here Router R3 and R4 are known as ABR (Autonomous Border Router). The routers belongs to a particular area are known as internal Router. So here R2, R5, R6 and R7 are internal router. Remember there should be at least an area remain Area ID 0 which is known as backbone Area of the network. The ABR router must have one interface belongs to an external Area.
I hope you found this article helpful related to basics of OSPF multi area network. For any query or suggestion on this article you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.





Great post. Articles which have meaningful and insightful comments are
more enjoyable, at least to me. It’s interesting to read what others thought
and how it relates to their customers, as their
perspective could possibly help you in the future.
King regards,
Harrell Valenzuela
Very interesting subject, appreciate it for putting up. “The height of cleverness is to be able to conceal it.” by Francois de La Rochefoucauld.