Contents of this article
In this article I describe the role and function of Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch in networking. Switch forwards the data packets within the same network. The data packets forwarded by switch on the basis of MAC table which is stored in its operating system. The basic functionality of switch is to forward the data packets to its destination by MAC filtering.
Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch connects two or more different devices within a local area network. Switch works like a relay for data transfer between end devices. When the destination of a data packet is beyond the LAN, the packet forwarded to the gateway router.
What Switch in networking?
A Switch is a device which works at Data link layer in networking. A Switch receive and transmit the data packets between different end devices. Switch inspect the header section of the received packet to check the destination IP address and MAC address then forward accordingly. A switch can connect the computers via Ethernet port, Fast Ethernet port and optic fibre port. Switch works on its operating software which store the MAC address of devices connected with the various interfaces of switch.
The layer 2 and layer 3 switch are always placed behind the gateway device. Router is generally used as gateway device for all data packets of a network. Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch works like a bridge between the multiple devices in a computer network. Switch are used to the basic data packet forwarding function to high end configuration switching. The latest switch are capable to create and works with VLAN in the network. The broadcast domain can break by creating the VLAN in switches.
Basic concepts of Layer 2 Switching
layer 2 switching done at data link layer in OSI reference model. Data link layer uses MAC address of devices for data transfer. Layer 2 switch break the collision domain. Each port of the layer 2 switch have its own collision domain. Instead of switch, HUB define all ports in a single collision domain. Hub works on physical layer.
Working of layer 2 switching
Before layer 2 switch, Old bridges were used in networking. Later switch replace these bridges. The bridges maintains content addressable memory filter table. This table was used to transmit the data to correct receiver. Layer 2 switches maintain MAC address table for same purpose. Layer 2 switch provides a fast speed data transmission in a network because its each port breaks the large collision domain.
Each port have its own collision domain. Layer 2 switch forward frames from one device to another. A router decide to forward or drop the packet on the basis of PUD attached with packet. This PUD have the IP address of source and destination. Layer 2 switch forward the frame on the basis of MAC address header on the frame. Layer 2 switch add MAC address of connected devices to its database itself automatically.
Functions at Layer 2 switching
The main functions of layer 2 switching are address learning, frame forwarding and loop avoidance. These three functions provides a fast and reliable data transfer in a network. Here we discuss in brief about these functions of layer 2 switching.
Physical address learning at layer 2 switching
Here physical address means MAC address. Layer 2 switch maintain a MAC address table. This table contains the MAC address of all connected device with the switch. When a frame received at any port of switch then switch filter the MAC address from the frame. If filtered MAC address is not stored in its MAC database then switch save the MAC address. This process done with each frame received by the switch. When a switch is powered on, its MAC address database remains empty.
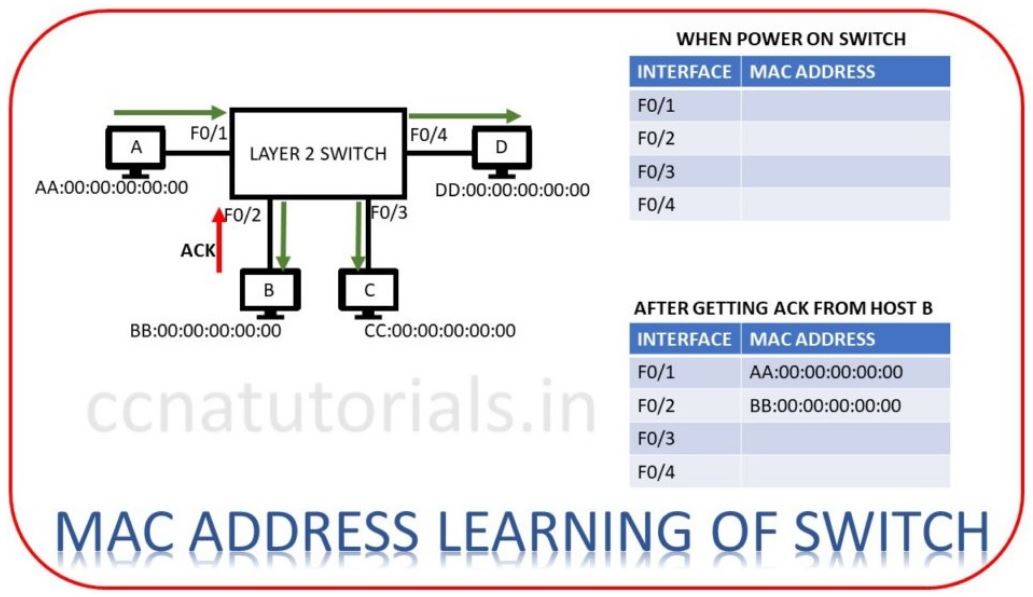
Now let’s device A want to transmit data for device B. Frame encapsulates device A at layer 2. Source address added to each frame transmitted via device A. Switch receive the frame at port F0/1.
As switch boot first time and have no MAC address database. Switch firstly save the mac address of device A from frame header. Now switch transmit the same frame to each device connected with it except to device A. Device B forward an acknowledgement frame to switch that the frame destination is device B. On getting this acknowledgement switch store the MAC address of device B in its MAC address database table. Next time when device A or B send data to each other, switch forward the frame to correct address according to MAC address table. We can say now device A and B can communicate point to point with each other. Same process done till the MAC address of each connected device stored in its MAC address table.
Forward and Filter Decisions at layer 2 switching
We know how a layer 2 switch create and maintains it’s hardware address table. Forward and filter decisions at layer 2 switching depends on MAC database table. When a frame received at its interface. Switch look after the destination MAC address in frame’ header. On finding the destination hardware address it choose the interface to exit the frame. Each frame treat according to this process and forwarded to correct device.
On receiving a frame switch forward it to correct exit interface. The frame does’t sent to any other interface except it’s correct destination. This process is known as frame filtering. If the MAC address is not found in MAC database then switch flood the frame to each port except the interface of frame source.
Loop Avoidance function on layer 2 switching
When multiple switches are connected in different segments then chances of Loop occurs in a network. Loop avoidance is important for better performance of the network. Spanning Tree Protocol is used to prevent the network loops. In large networks redundant links used between switches to avoid communication failure. Redundant links meaning if a link failed due to any reason next link will active automatically. Chances of communication failure are less. Sometime the redundant links creates network loop. This is because frames can be transmitted to all redundant links and creating loops. As shown in figure below.
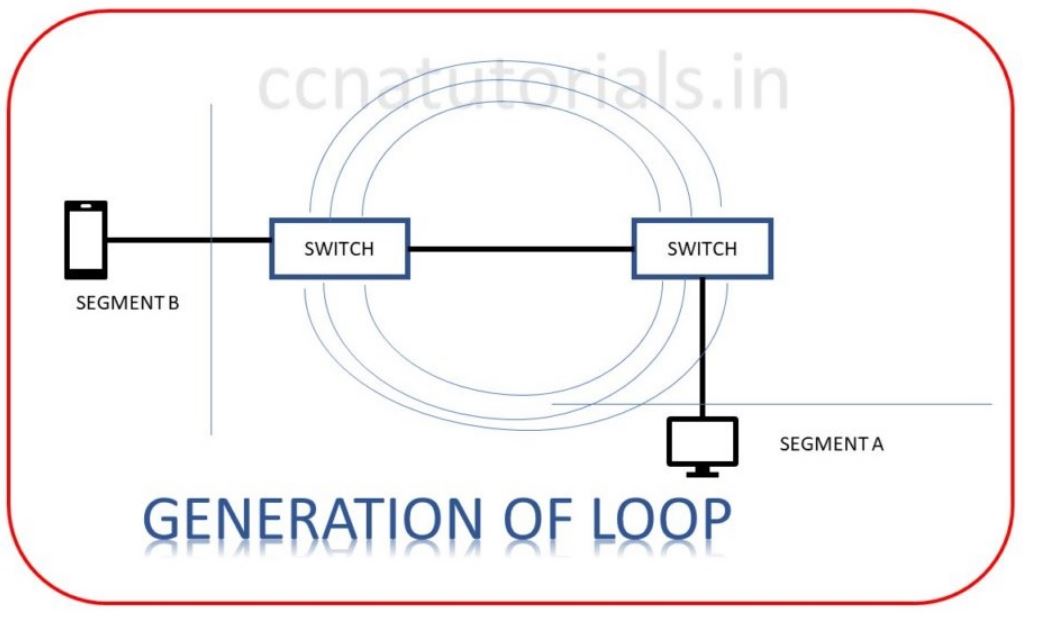
A host receive multiple copies of the same frame from different segments. Switch will not filter the frame because frame received from multiple interface on switch. Switch will save the mac address of multiple frame and fail to forward the frame. This is known as thrashing the MAC table. This will creates a big flood of unnecessary data in the network. Poor performance slow speed will occur. One remedy to avoid loop back is to reboot the switches of any one segment. But in a large network rebooting of switch is a big deal. To avoid these problems spanning tree protocol used.
Switching at layer 3
Layer 3 switch are capable to do routing of data packets in a network. Opposite to layer 2 switch a layer 3 switch use the IP address along with MAC address for forwarding the data packets in the network. Layer 3 switch can create and store the VLANs which breaks the big broadcast domain into small broadcast domains. The data transfer speed of Layer 3 switch is very fast then layer 2 switch. The address learning and loop avoidance feature of layer 3 switching is very similar to the layer 2 switching.
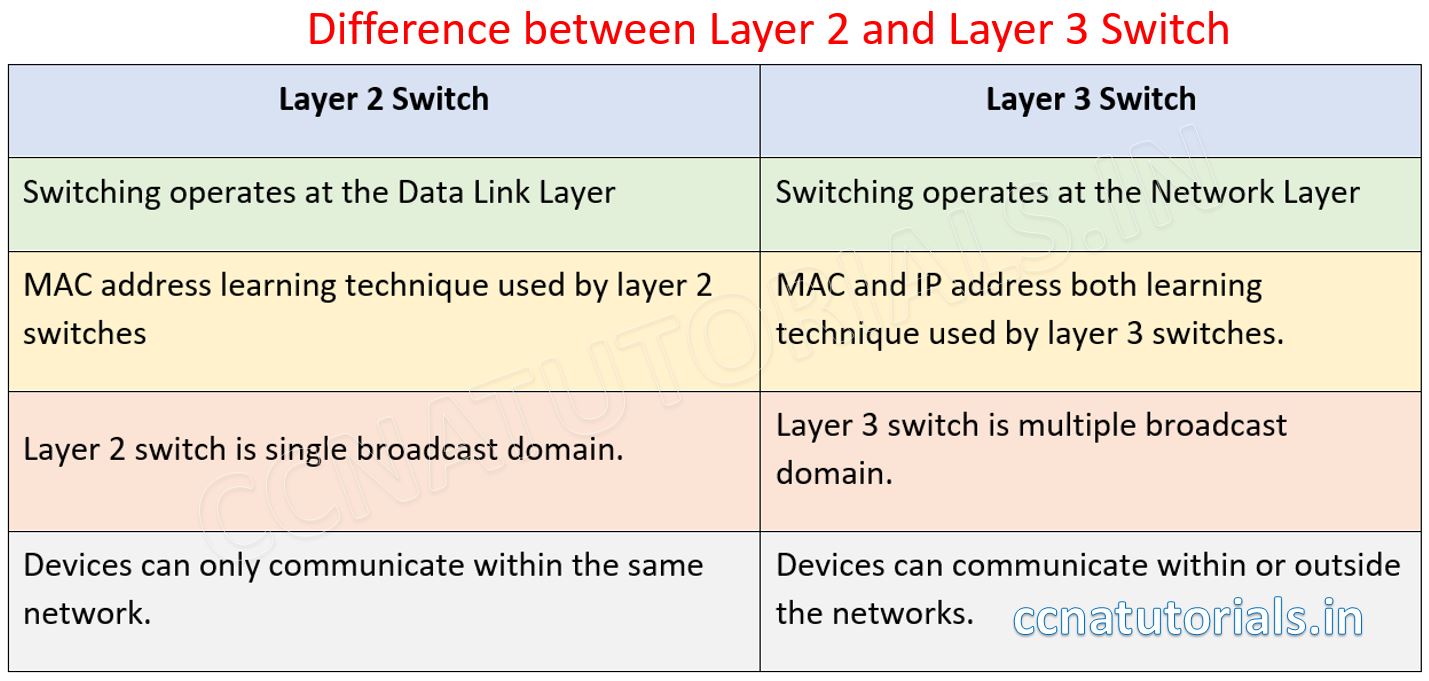
Difference between layer 2 and layer 3 switch techniques
Layer 2 switching is based on the MAC address of source and destination. Data packets simply received and forwarded within the network. While layer 3 switching is based on IP address and MAC address.
Layer 3 switch used various protocol to receive and forward the data packets. While the Layer 2 switch only forward the data packet to its destination. The purpose of Layer 2 and layer 3 switch is same in the network.
Layer 2 switching is purely MAC address learning technology. While the layer 3 switch uses the ARP to determine the MAC address of a device connected with any interface. ARP is acronym of Address Resolution Protocol. The data transfer speed of layer 2 switching is fast than layer 3 switching because in layer 2 switching the data packet processed only two layer. In layer 3 switching the data packets process up to 3 network layers.
I hope you found this article helpful related to the basics of layer 2 and layer 3 switch. For any query or suggestions you may contact us or drop a comment below. Your suggestions are always welcome by us. Keep continue reading.






Hi,
Firstly, thank you for sharing the CCNA information.
Your article is easy understanding and I’d love it 🙂
However, there’s one section in *Switching at layer 3* paragraph mentioned “The data transfer speed of Layer 3 switch is very fast then layer 2 switch.” while
below section in *Difference between layer 2 and layer 3 switch techniques* paragraph no.3 mentioned “The data transfer speed of layer 2 switching is fast than layer 3”.
This part is confusion. Please advise.
Thank you.