In this article I describe the Link State Routing Protocols in networking for CCNA exam. Link State Routing Protocols belongs to Dynamic Routing in router. We can configure the IP routing in router manually or dynamically. Static IP Routing in router perform the packets transfer very efficiently in small network. It is very difficult to configure and maintain the static IP Routing in router for large networks.
We required an automatic method of routing in routers in large networks. So we use the dynamic routing in big networks one of them are distance vector routing protocols and other one is Link State Routing Protocols. Basically routing is necessary to flow the data packets from one network to another network. We configure the routing table in routers to achieve the aim.
Link State Routing Protocols helps to select the path for data packets in network. Routing table of routers updates automatically from one router to other routers in a large network by using the Link State Routing Protocols. Routers are self responsible to transmit the new update in routing tables. Dynamic routing protocols dynamically select the network distance and other factors for data flow in a large network. It will be helpful to know about the dynamic routing in router alongwith the Link State Routing Protocols.
Dynamic routing in router explained
Maintenance of routing table in all routers in a network is very critical job. Dynamic IP Routing in router make it easy to maintain the routing table in all routers in a network. Dynamic routing protocols make it easy to take decision to select the best path for data packets. The routers transmits and receive the routing information in a fix time interval and update the routing table.
Any change in network is immediately updated in all routers by sharing information. The drawback of dynamic routing is that more bandwidth consumed than static routing. Dynamic routing make easy to maintain the routers in large network. When a router gone defective or new router added in network, the dynamic protocols updates the routing table in all routers in network. The routers exchange the network update between each other by broadcasting and multicasting.
Example of Dynamic IP Routing in router
In static routing we configure the route in routers manually. Some dynamic routing protocols help to do the job of static routing in all routers in a large network. RIP (Routing information protocol) OSPF ( Open Shortest Path First) are example of dynamic routing protocol. Dynamic routing protocols are further used two methods for sharing the routing information. Distance-vector and Link-State routing protocols used different technique for sharing route table information.
Distance-Vector and Link-State protocols
Distance-Vector routing protocols select the best path for data packets. Here distance is reference of hop in network. Distance-Vector protocols calculate the distance between source and destination on the basis of hop count. Suppose there are two path available for data packet from source and destination. Distance-Vector protocol select the path in which the number of hopes are less. RIP and IGRP are example of Distance-Vector routing protocol.
Link-State routing protocols does not work on hope count measure. Link-State routing protocols use the topology of internetwork. Topology means the speed of interface and administrative distance etc. OSPF is the example of Link-State protocol. In large network both Distance-Vector and Link-State used together for better performance in network. EIGRP and RIPv2 are example of hybrid protocols used in large networks. In next articles we discuss in brief about the Distance-Vector and Link-State routing protocols.
Link State Routing Protocol in brief
Link State Routing Protocols used to select the path for data packet in an internetwork. Link state routing protocols uses link state routers to share information of connected network devices. This is a learning process. By learning process each router maintain the routing table to select the shortest path for data packet transmission. Link state routing protocols can handle a large network. Link state routing protocol works on network topology. Each router update the network topology to nearby router only. Link state routing protocols are also known as shortest path first protocol.

Link state routing protocols explained
Link state protocols allow routers to share the information about network connected to it. This information passed to neighbour router only. An accurate information of network topology around the router updated in routing table. By help of the routing table better routing path selected by the router.
The information passes by router is known as link state advertisements(LSAs). In distance vector the information message passes in a fix time interval. Link state advertisements shared only when any changes done in the network topology. The bandwidth less consumed by link state routing protocol. The time of convergence is less than in distance vector protocol.
Function of link state routing protocol
Important terms of link state routing protocol are link state packet, database, algorithm, routing table etc. Link state packets contains the routing information and sent to neighbour only when any changes occurs in connected network. Link state packets update the routing table in nearby routers. The information collected by link state packets stored in link state database.
Link state database maintained in each link state enabled router. When a link state packet received by a router, the link state database updated automatically. This link state database help to select the shortest path first. This algorithm is known as Dijkstra algorithm. Routing table maintained in each router. Routing table stores the information of known path and interfaces of router. The best example of link state routing protocol is Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
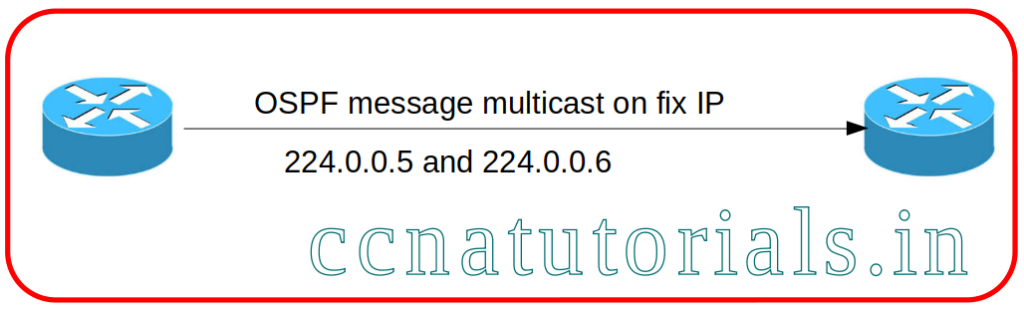
link state routing protocol OSPF
OSPF use advertisement and acknowledge packets to keep update the neighbour router’s routing information. When any interface or router goes down, the information about it is immediately advertise to the nearest router. This information updated in all routers in the network. This is known as network convergence.
OSPF supports the classfull and classless networks. OSPF is an intradomain routing protocol. As mentioned above OSPF supports classless network it means the IP packets contain both IP address and subnet mask of destination network. The link state messages are broadcasts on specific addresses 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6.
I hope you found this article helpful related to Link state routing protocols. For any query or suggestion on this article you may contact us or drop a comment below. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.






