Contents of this article
In this article I describe the basics of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP. Routing protocols helps router to build and maintain the routing table in routers. Routing protocols are one important part of default routing in router. Routing protocols inform the router about the networks connected at each interface. Routing protocols doesn’t carry or push the data packets in any way. Any change in the network required to be update in the routing tables of all routers. This task is carried out by the routing protocols. Routing protocols help the routers to select the best path to exit the data packets.
Example of routing protocols are RIP, RIPv2, IGRP,OSPF etc. Routing protocols further divided into distance vector, link state and hybrid protocols. These all routing protocols update the routing table of all routers in the network. You can see the routing protocols by “show ip route” command in privilege command mode of router. Routing protocols are not responsible for data packet flow in any way. Routing protocols spread the information of network hierarchy to all routers.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
EIGRP is a network protocol which allow computers to share the information between different networks. EIGRP protocol allow a router to keep a copy of next hope router’s routing table. Each router keeps a copy of routing table of neighbour router. EIGRP is a dynamic routing protocol developed by Cisco Systems. Initially the EIGRP protocol was only supports the Cisco devices but later in 2013 it became an open standard for many other devices also.
Basic features of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
EIGRP is a classless distance vector protocol. Administrative Distance of EIGRP is 90 and 170. AD is 90 in case of the routers are connected in the same autonomous and 170 in case of the routers are connected in the different autonomous. EIGRP works as distance vector and link state routing protocol too, so it is some time also known as hybrid protocol. EIGRP supports the VLSM or classless routing CIDR.
The selection of best path from source to destination is done by Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL). The multicast IP 224.0.0.10 used by the routers to update each other. EIGRP supports all network layer protocol such as IP, IPv6, IPX and AppleTalk. The maximum hop count for EIGRP are 255 which remain 100 by default. EIGRP creates neighbour table, routing table and topology table. EIGRP used Reliable Transport Protocol RTP for communication between routers.
Types of Packet used by Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
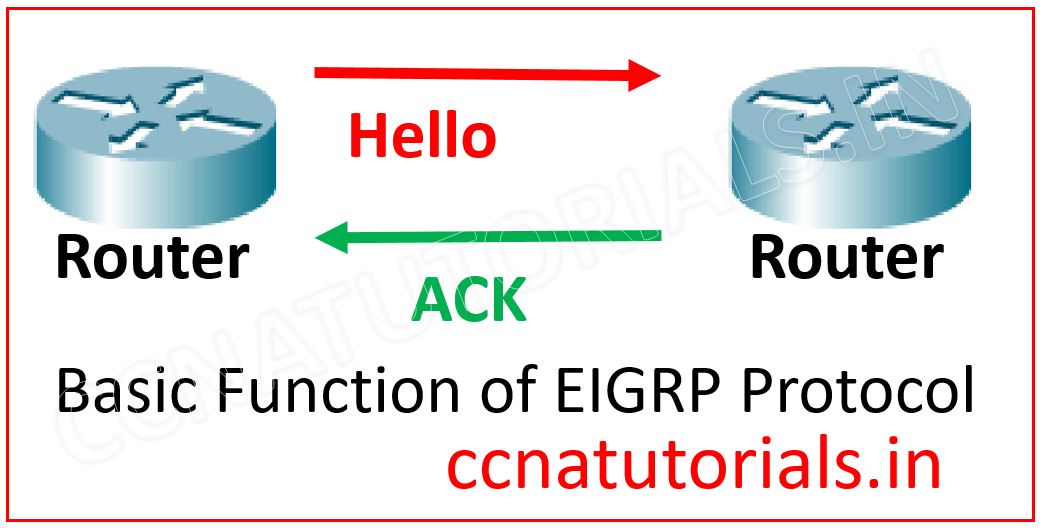
EIGRP used mostly five types of packet for its operation. These packets are Hello, Update, Query, Reply and Ack.

Hello packet intimates the neighbour router about the alive mechanism. When a router do not respond to the hello packet it means its services are down. Update packets are used to update the routing table when a new network device connected in the network or the network topology changed due to any reason. Query packets are used to make request for some specific information from the neighbour router. In respond to any query the reply packets are send with the required information. ACK packets are the acknowledgement packet after getting the reply packets.
Neighbour discovery in EIGRP operation
Routers exchange the routing table with their neighbour routers. Link state protocols use hello packets to keep update the neighbour router. The neighbour updates when any changes happens in the existing network topology. When a new network device added in the network or any existing device removed or down due to any reason. The hello packets frequency is 5 second default. Another term is hold time used by the router to consider the neighbour router is out of service.
If a router do not receive the hello packet up to 10 seconds from a neighbour router, it consider it dead. In this condition the routing table updates and the updated routing table shares with the neighbour routers by EIGRP. So all the routers in the network know about the dead router and keep changes in their own routing table.
Similar action done when a new router added in the network. When a router added in network it sent hello packets to its neighbour. On getting hello packets the neighbour update its routing table and sent the same to other neighbour. This process done until the routing table of all routers not updated.
Reported and Feasible distance in Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
There are two metrics consider in the term of distance in EIGRP. The one is reported distance and another is feasible distance. The total distance between source and distance is known as feasible distance and the distance from the neighbour to the destination is known as reported distance. See the example below.
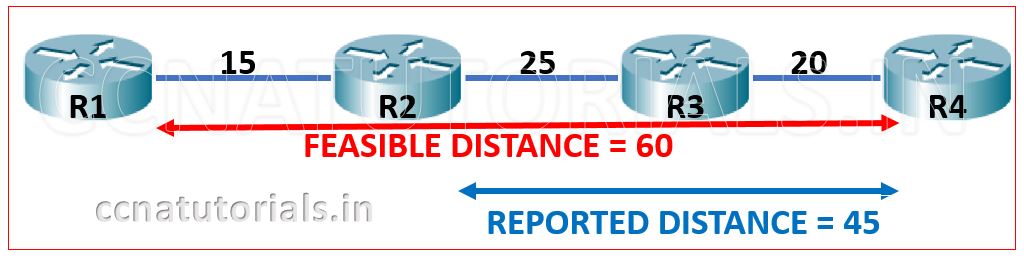
Here the source is router R1 and the Destination is the Router R4. The distance metrics is shown in the diagram. So here the feasible distance is 15+25+20=50 and the reported distance is 25+20=45.
Neighbour and topology table used in Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
There are two terms which are very important are neighbour and topology table. In Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP each router keep information of its nearest neighbours by using some hello packets. When a neighbour router become dead or a new one is added, the changes are recorded and added to the neighbour’s routing table. The update keep remains in a sequence in the neighbour table. The latest sequence record considered as the latest record.
The topology table used to select the best path for data sending. Actually the Diffusing Update Algorithm DUAL and topology table both decide the best path for sending the data over the network. The neighbour and topology table stored in RAM of the router.
Feasible Successor and Successor in Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP
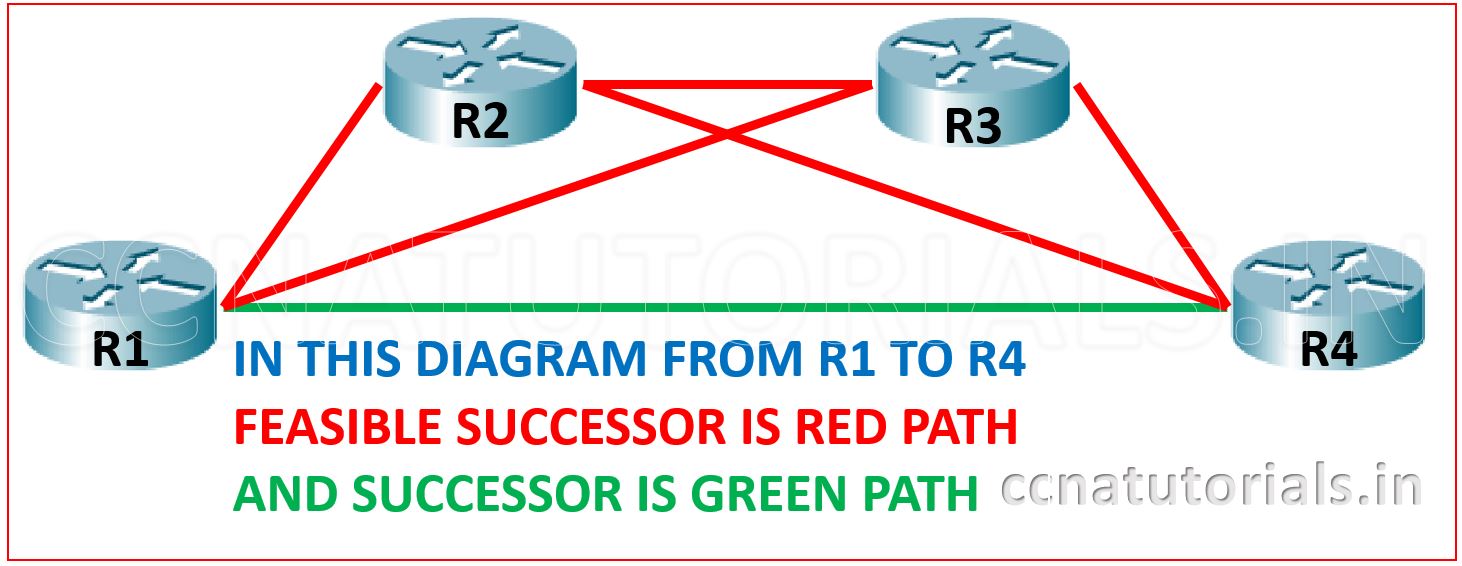
In a network from source to destination there may be many path available. Some of them are selected by using some metrics and some of them keep as backup path in case of failure or any root path. So basically the feasible successor are the possible paths which are available between source and destination.
Feasible successor stored in the topology table as a backup path for any source to destination. The successor is the best single path selected according to DUAL and RD/FD for data transmission from source to destination. See the below image to understood the feasible successor and successor in Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol EIGRP.
So in this article I describe some basic terms and benefits of EIGRP. I hope you found this article helpful. For any query and suggestion you may drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome from us.





