Contents of this article
In this article I describe the Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP. HSRP is a routing protocol which provide redundancy to the hosts. Hot Standby Router Protocol is a Cisco proprietary. HSRP allow multiple routers to work like a single virtual router. The main benefit of Hot Standby Router Protocol is if a router failed then other router takes place of failed router. HSRP can be configured on Ethernet, FDDI or Token ring in local area network. Hot Standby Router Protocol provides automatic backup of router configuration.
Hot Standby Router Protocol allow to forward the packets from only single router which is known as active router. HSRP define the mode of router it may be active or standby. So active router is on the work of packet forwarding, in case of active router fails the standby router starts working in place of active router. So we can say the Hot Standby Router Protocol is a redundancy mechanism in Cisco routers.
Client redundancy problems
Before going to Hot Standby Router Protocol in brief let’s take a look on the client redundancy issues. Is there any option to send the data in case of failure of default gateway? The first thing came to mind is it is not possible. We have only one option in this case and that is to replace the router with a new one. To overcome these issues we use two routers as gateway. One is active and other is standby. See the image below.
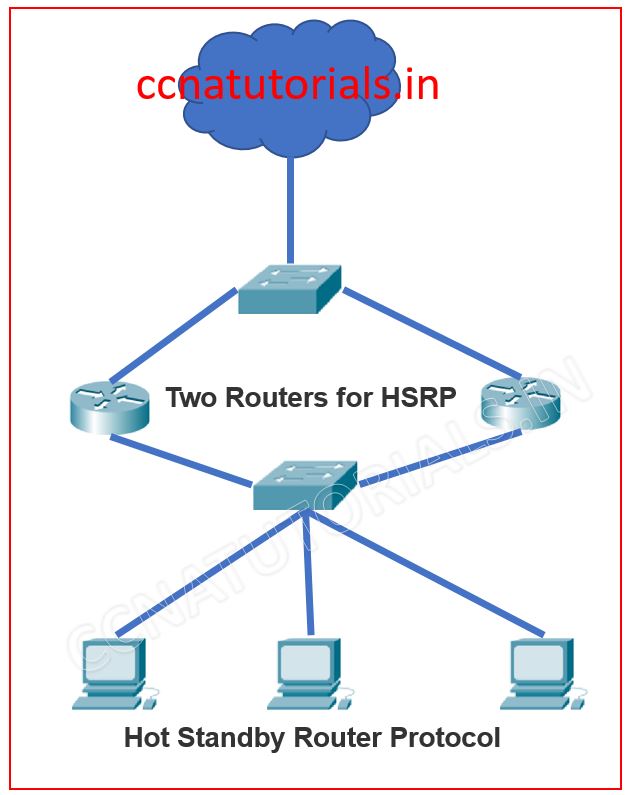
There are many protocols which are used for redundancy problems in network. Some of them are HSRP, VRRP and GLBP but in the syllabus of CCNA only HSRP is required.
Hot Standby Router Protocol explained
Hot Standby Router Protocol is a Cisco proprietary protocol. A standby group is create by HSRP protocol. Each standby group includes the Active router, standby router and virtual router. There is one router defined as active router and other two or more routers defined as standby routers. A term HSRP Timers is used in Hot Standby Router Protocol. HSRP timers ensures communication between the routers. In case of failure of active router HSRP timers allow standby routers to take over.

Hello, Hold, Active and Standby are the basic function used by hello timers. Hello message ensure the state of routers. A Hello message sent on a fix time interval of 3 seconds. Hold timer ensure the state of active router. Hold time is generally 10 seconds, it means if there is no any response of hello message up to 10 seconds than the active router declared out of service. Active is also check the state of active router. Standby timer monitor the condition of standby router.
Virtual router used in Hot Standby Router Protocol
Virtual router is a virtual entity in the network. There are two router one is active and other is standby. A client don’t need to change the default gateway in network address section. HSRP is responsible to make sure the virtual router is available to clients. Virtual router works like active router. The packets of the clients forwarded to the IP address of virtual router.
Active and Standby router in Hot Standby Router Protocol
Active router is currently working physical router. The Active router received and forward the data traffic of its clients in the network. Active router used the IP address and MAC address which are defined for virtual router. Active router also reply to the ARP requests on the network.
Standby router are the physical routers which remains in standby mode until the active router works fine. In case of failure of active router the standby router take over the function of active router. The virtual IP and MAC address captured by the standby router and the data flow remains continue for the clients of the network.
Configuration of HSRP
The configuration of HSRP in a router is very easy. We can configure the HSRP in router with the help of some couple of commands. I take a scenario as shown in the picture below.
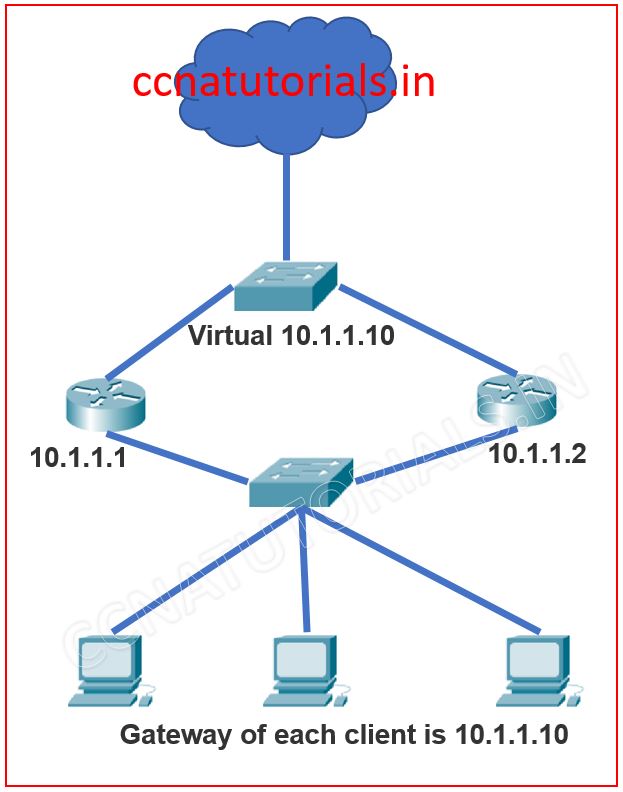
Here two physical routers used for redundancy of clients data in the network. Both routers connected as gateway for the local area network. But at a particular time only active router works. The other router remains in standby condition. The connected ports with LAN defined the other IP address than the gateway of clients. Here the gateway of clients is virtual IP address which we define in the configuration of HSRP in both routers.
The syntax of HSRP command is “standby [group] [ip] [virtual ip]”. So see the below commands run in the router1.
router1>en router1#config t router1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/0 router1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 router1(config-if)#no shut router1(config-if)#standby 0 ip 10.1.1.10 router1(config-if)#standby 1 preempt router1(config-if)#standby priority 110 router1(config-if)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] router1(config-if)#exit router1(config)#exit
To check the status run the below command in router1 CLI
router1#show standby GigabitEthernet0/0/0 - Group 0 State is Active
Same commands required to be run in router2. See the below command window.
router2>en router2#config t router2(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/0 router2(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 router2(config-if)#no shut router2(config-if)#standby 0 ip 10.1.1.10 router2(config-if)#standby 0 preempt router2(config-if)#standby priority 110 router2(config-if)#do wr Building configuration... [OK] router2(config-if)#exit router2(config)#exit
To check the status run the below command in command line of router 2
router2#show standby GigabitEthernet0/0/0 - Group 0 State is Active
You can see the configuration of HSRP is done in both routers. Now the client works with the default gateway 10.1.1.10 which is actually a virtual IP address configured in both routers.
I hope you found this article helpful related to the HSRP protocol from this article. For any query or suggestion drop a comment below or contact us. Your suggestions are always welcome by us.



