In this article I describe the term IP Routing Process in router related to networking. IP Routing Process in router belongs to IP routing in router. IP Routing Process in router is a process of packet transfer between different networks via a router. When we access the internet or intranet the data packets transmitted and received by IP Routing Process in router.
Every interface of router has a different network. Routers are also known as layer3 device. Various routed and routing protocols used for moving packets between different networks. Generally the IP Routing Process in router is done by static routing, default routing and dynamic routing protocols.
Requirement of IP Routing Process in router
The function of a router is to move the data packets from one interface to another interface or we can say between different networks. The movement of packets done at layer 3 which is known as network layer of the OSI reference model. Router keep the information of neighbour router and network in its routing table.
There may be many interfaces in a router which connect different networks. How the router moves the packet to its destination it depends on routing and routed protocol. Static route in a router is a set of protocols which allow the router to transfer the packet to its destination. To understand the IP Routing Process in router it is necessary to know about the routing and routed protocol firstly.
Routing protocol for IP Routing Process in router
Routing protocols helps router to build and maintain the routing table in routers. Routing protocols are one important part of default routing in router. Routing protocols inform the router about the networks connected at each interface. Routing protocols doesn’t carry or push the data packets in any way. Any change in the network required to be update in the routing tables of all routers. This task is carried out by the routing protocols. Routing protocols help the routers to select the best path to exit the data packets.
Example of routing protocols are RIP, RIPv2, IGRP,OSPF etc. Routing protocols further divided into distance vector, link state and hybrid protocols. These all routing protocols update the routing table of all routers in the network. You can see the routing protocols by “show ip route” command in privilege command mode of router. Routing protocols are not responsible for data packet flow in any way. Routing protocols spread the information of network hierarchy to all routers.
Routed protocol for IP Routing Process in router
Routed protocol works with the data packets for default routing in router. Routed protocol sends the data packets within a router’s interfaces. Routing protocol decide the best path and routed protocol send the packets on these paths. Routed protocols are defined on interfaces of router. Routed protocols do not update or maintain the routing table in a router. Routed protocols are responsible for flow of data packets from one network to another network.
Routed protocols sends the data packets to correct exit interface of the router. Routed protocols are configured on interfaces of the router. Example of routed protocols are IP, IPv6, IPX and Appletalk. Routed protocols are basically addressing schema of the interfaces of router. Router identify the destination network of a data packet and send the data packet to correct exit interface. The concept of subnetting takes place in routed protocols.
Fundamentals of IP Routing Process in router
We know that routers used to connect the different LAN and WAN. We required to connect the different network with a router physically firstly. After completion of physical connectivity next step is to configure the logical network addresses and routing protocols. Each LAN or WAN works in a fix network ID. In case of router I mention the network ID for each LAN. When we work in a LAN, I mention the IP address for each host. Each host assigned a gateway which is the interface of the router to out the packet from that LAN. Router do not forward the packet to host. Router transfer the packet for network ID.
The flow of packets between different LAN depends on destination address on the packet. All routers maintain the routing table to determine the best route to remote network. Routing protocol keep update the routing table in IOS of router. The routing table help to find the destination network of a packet. Basically multiple protocols works for dynamic routing in router to transfer the data between different networks.
IP Routing Process in router explained in brief
Data packets transfer between two different networks done by IP routing process in router. A router transfers the data packets between different networks. There are various protocols responsible for data packet transfer between interfaces of routers. In this article I will take very simple network topology to explain the IP routing process in router. The network designed as shown in picture below. Two different networks 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 are connected with a router. We take example of ICMP packet routing between both network.
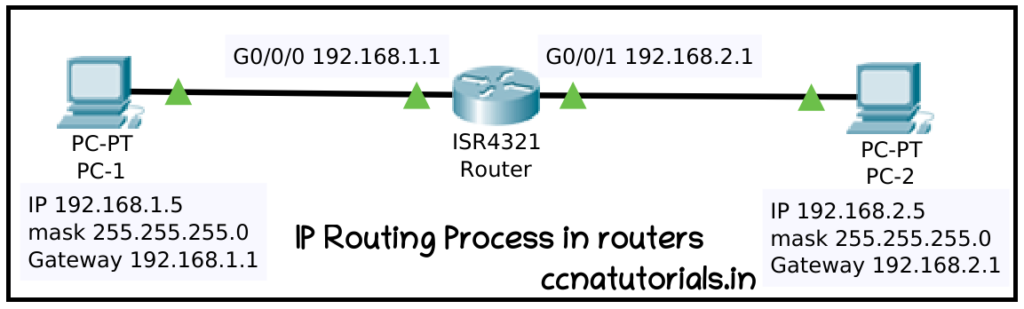
See the image above the IP address of PC1 is 192.168.1.5/24 and gateway is 192.168.1.1. The IP address of GigabitEthernet0/0/0 is 192.168.1.1. similarly the IP address of PC2 is 192.168.2.5/24 and gateway is 192.168.2.1. The IP address of GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is 192.168.2.1. After configuring the above IP addresses PC1 is enable to ping PC2 without configuring any routing. Communication between PC1 and PC2 is possible because both network are direct connected with the router. Run the sh ip route command in router to see the connected network.
Router#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0 L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0 192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1 L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Router#
you can see above result of connected networks with the router. PC1 is enable to ping PC2. Now I am going to explain step by step how Ping works via ip routing process in router? Ping command send and receive the ICMP packets from a destination device. Here the source is PC1 and destination is PC2. Following IP routing process take place during the whole communication between PC1 and PC2.
Step 1 of IP routing process in router
An ICMP packet generates in PC1 when ping 192.168.2.5 command executed. This ICMP packet search for mac address belongs to ip address 192.168.2.5. This IP address is not available in the same network so PC1 broadcast a request to get the mac address in the network by ARP request. Router got the request and send reply with mac address of GigabitEthernet0/0/0 interface.
Step 2 of IP routing process in router
After getting the mac address of gateway interface the packet hand over to the data link layer. The ICMP packet breaks into frame with MAC address of PC and destination mac address of gateway interface G0/0/0 of router. The frame handed over to physical layer for transmitting it towards gateway interface G0/0/0 of router. Physical layer transmit the frame towards gateway interface of router in the form of binary bit stream.
Step 3 of IP routing process in router
The binary bit stream received on interface G0/0/0 of router. Interface G0/0/0 build frame from the binary stream bits and run CRC and FCS for checking the error correction in frame. Router check the destination address on the frame and check it’s routing table for destination address. Router found the destination address network is connected to its other interface G0/0/1. Router forward the frame to other interface to provide the exit path to frame. If the destination network not found in routing table the frame will be drop by router and a message of destination not reachable sent to PC1.
Step 4 of IP routing process in router
The interface G0/0/1 further check the destination address of packet and convert it into frames. Interface G0/0/1 check the ARP cache to find the mac address of destination address 192.168.2.5. If router found the mac address in ARP cache it will forward the packet to that mac address. In case the mac address is not available in ARP cache the router broadcast ARP from G0/0/1 to get the mac address of 192.168.2.5 interface of PC2.
Step 5 of IP routing process in router
PC2 responds with MAC address to the ARP request of interface G0/0/1 and send the mac address of its ethernet port. After getting the mac address router send the packet frame to PC2 in the form of binary bit stream.
Step 6 of IP routing process in router
On receiving the binary bit stream the enternet port of PC2 create fram and check the FCSand CRC for error correction in the received frame. Frame than build the packet and ethernet port of PC checked the packet. On getting the information of packet that it is ICMP packet. PC2 needs to send the reply of this ICMP packet to PC1.
The above 5 steps repeat again but now in reverse side from PC2 to PC1. Finally PC1 got the ICMP echo-reply of ping command from PC2. These are the ip routing process done in routers during transmitting a packet. I hope you found this article helpful for the exam purpose of CCNA certification.
I described the IP routing process in router step by step related to networking fundamentals. For any query or suggestion on this article contact us or drop a comment below. your suggestions are always welcome by us.






